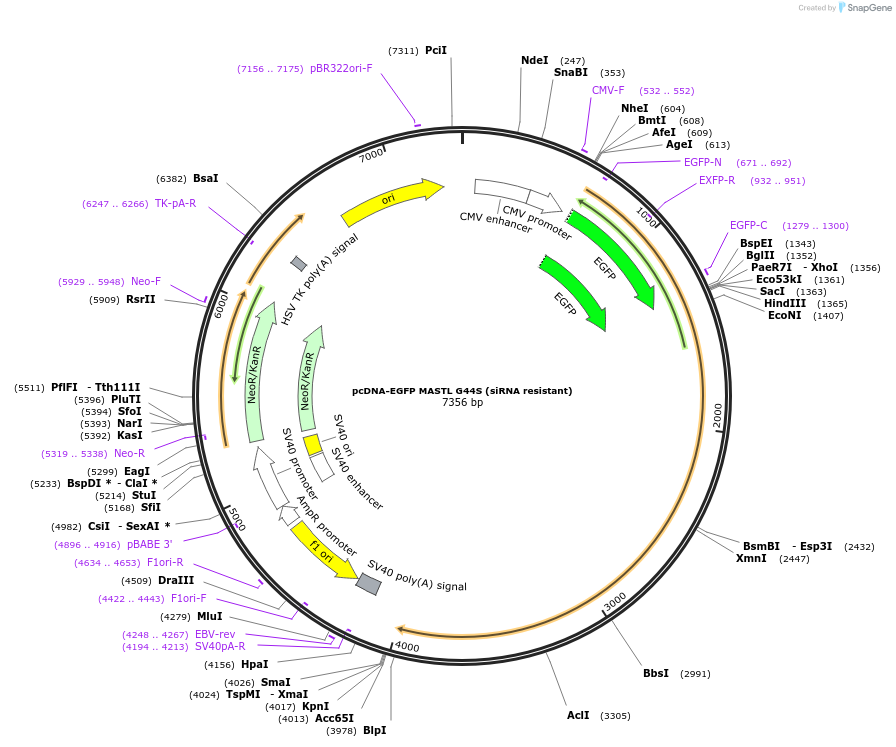
pcDNA-EGFP MASTL G44S (siRNA resistant)
(Plasmid
#191012)
-
PurposeExpresses EGFP-tagged kinase-dead MASTL G44S with resistance to MASTL siRNA (ACGCCTTATTCTAGCAAATTA)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 191012 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepEGFP-C2
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4735
- Total vector size (bp) 7356
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameMicrotubule-associated serine/threonine kinase like
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
MutationG44S
-
GenBank ID84930
-
Entrez GeneMASTL (a.k.a. GREATWALL, GW, GWL, MAST-L, THC2)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer EGFP_C
- 3′ sequencing primer SV40pA_R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pcDNA-EGFP MASTL G44S (siRNA resistant) was a gift from Johanna Ivaska (Addgene plasmid # 191012 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:191012 ; RRID:Addgene_191012) -
For your References section:
MASTL promotes cell contractility and motility through kinase-independent signaling. Taskinen ME, Narva E, Conway JRW, Hinojosa LS, Lilla S, Mai A, De Franceschi N, Elo LL, Grosse R, Zanivan S, Norman JC, Ivaska J. J Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 1;219(6). pii: 151688. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906204. 10.1083/jcb.201906204 PubMed 32311005