-
PurposeMammalian Expression, Bacterial Expression
-
Depositing Lab
-
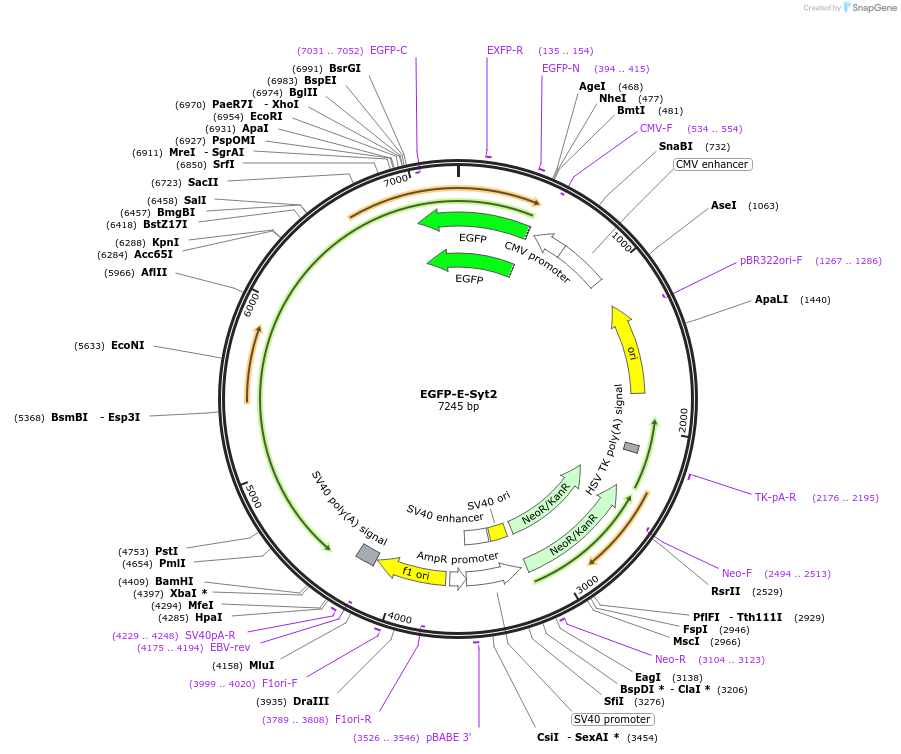
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 66831 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepEGFP-C1
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameE-Syt2
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
GenBank IDNM_020728.1
-
Entrez GeneESYT2 (a.k.a. CHR2SYT, E-Syt2, FAM62B)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- GFP (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BamHI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CAAGCTTCGAATTCgatgacgccaccgtcccgggc
- 3′ sequencing primer GATCCGGTGGATCCctatgtcatcgcctgaggcctc
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note that the E-syt2 coding region starts at the second methionine (M49) compared to the NCBI reference sequence; this shorter protein aligned more closely with endogenous E-Syt2 in SDS-PAGE. Both longer and shorter constructs displayed the same subcellular localization. Please see the associated publication for additional details.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
EGFP-E-Syt2 was a gift from Pietro De Camilli (Addgene plasmid # 66831 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:66831 ; RRID:Addgene_66831) -
For your References section:
PI(4,5)P(2)-dependent and Ca(2+)-regulated ER-PM interactions mediated by the extended synaptotagmins. Giordano F, Saheki Y, Idevall-Hagren O, Colombo SF, Pirruccello M, Milosevic I, Gracheva EO, Bagriantsev SN, Borgese N, De Camilli P. Cell. 2013 Jun 20;153(7):1494-509. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.026. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.026 PubMed 23791178