-
Purposeexpresses CD4 with C-terminal FLAG tag
-
Depositing Lab
-
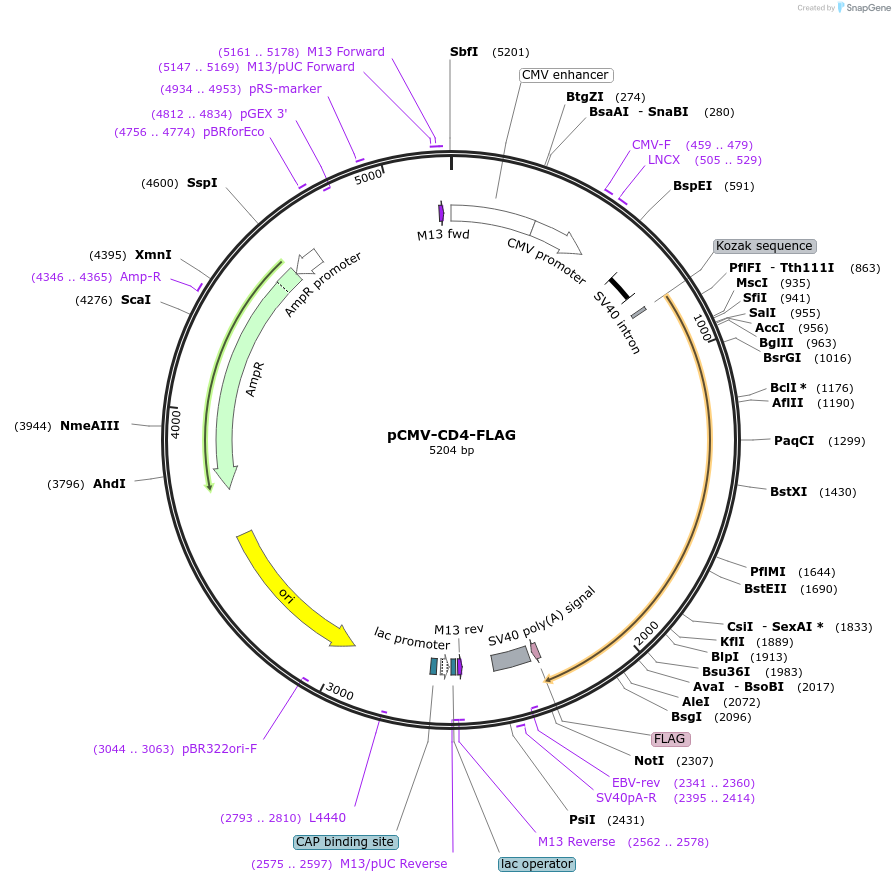
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 51604 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMV
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4000
- Total vector size (bp) 5300
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Stbl3
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCD4
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1300
-
GenBank ID
-
Entrez GeneCD4 (a.k.a. CD4mut, IMD79, Leu-3, OKT4D, T4)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- FLAG (C terminal on insert)
- myc (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BglII (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer gagacacggagagggtcttc
- 3′ sequencing primer CATTCTAGTTGTGGTTTGTCC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note that the sequence of the myc epitope tag in this plasmid is MQKLISEEDLL, which differs from the standard EQKLISEEDLL.
The CD4 insert in this plasmid contains N64I and K385E mutations when compared to GenBank reference sequence NP_038688.2.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV-CD4-FLAG was a gift from Suzanne Paradis (Addgene plasmid # 51604 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:51604 ; RRID:Addgene_51604) -
For your References section:
Sema4D localizes to synapses and regulates GABAergic synapse development as a membrane-bound molecule in the mammalian hippocampus. Raissi AJ, Staudenmaier EK, David S, Hu L, Paradis S. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov;57:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Sep 10. 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.08.004 PubMed 24036351