-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
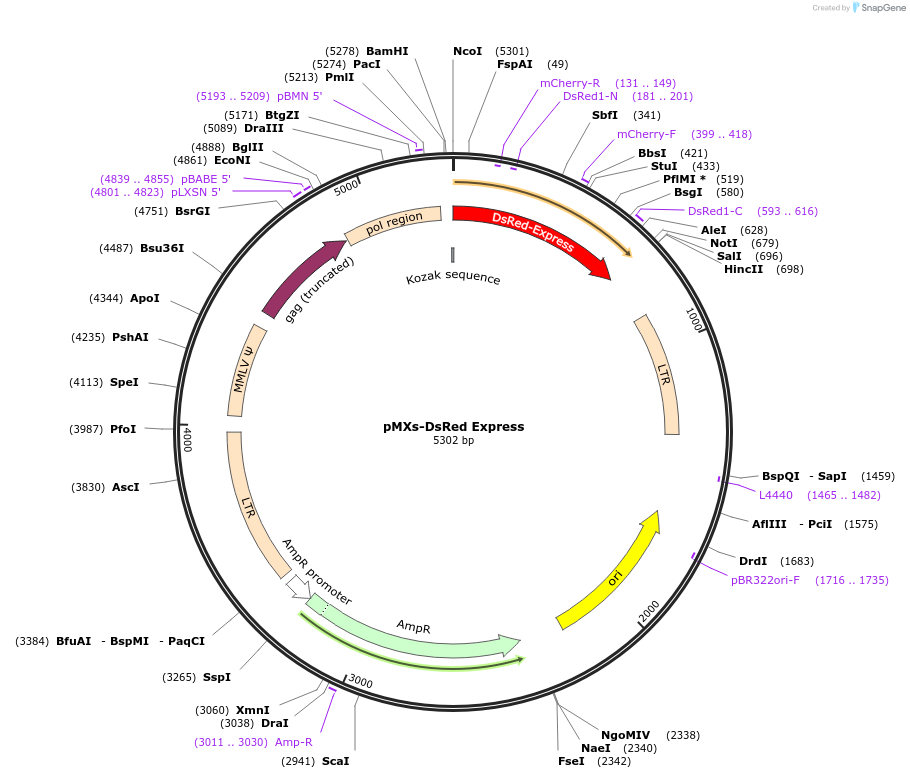
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 22724 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepMXs
-
Backbone manufacturerDr. Toshio Kitamura of the University of Tokyo
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4800
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Retroviral
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namea variant of Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein
-
Alt nameDsRed-Express
-
Speciesmushroom
-
MutationN/A
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer pMX-S1811
- 3′ sequencing primer pMXs-AS3200 (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Addgene Notes
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made bypMXs is from Dr. Toshio Kitamura of the University of Tokyo, the Institute of Medical Science. If you use this plasmid in a paper, please cite: Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning: powerful tools in functional genomics. Exp Hematol. 2003 Nov;31(11):1007-14. Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, Oki T, Nakajima H, Nosaka T, Kumagai H.
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pMXs-DsRed Express was a gift from Shinya Yamanaka (Addgene plasmid # 22724 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:22724 ; RRID:Addgene_22724) -
For your References section:
Suppression of induced pluripotent stem cell generation by the p53-p21 pathway. Hong H, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Kanagawa O, Nakagawa M, Okita K, Yamanaka S. Nature. 2009 Aug 27. 460(7259):1132-5. 10.1038/nature08235 PubMed 19668191