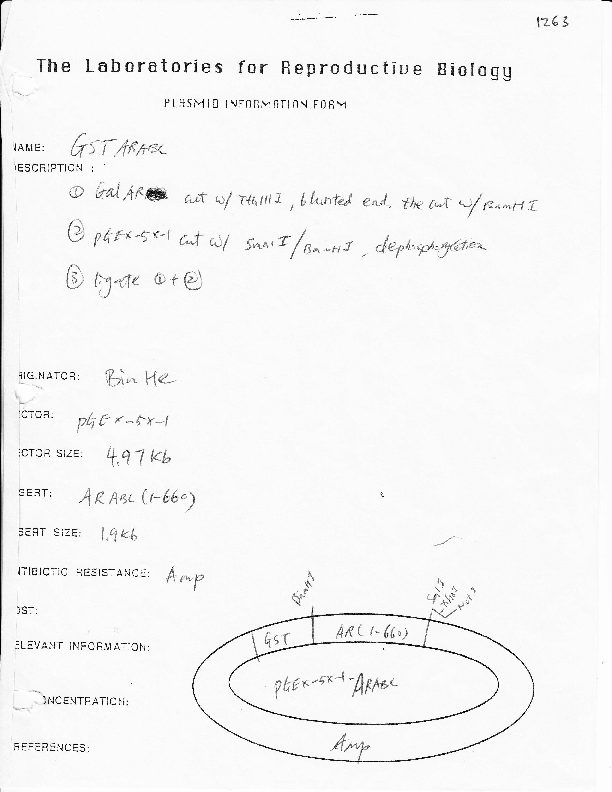
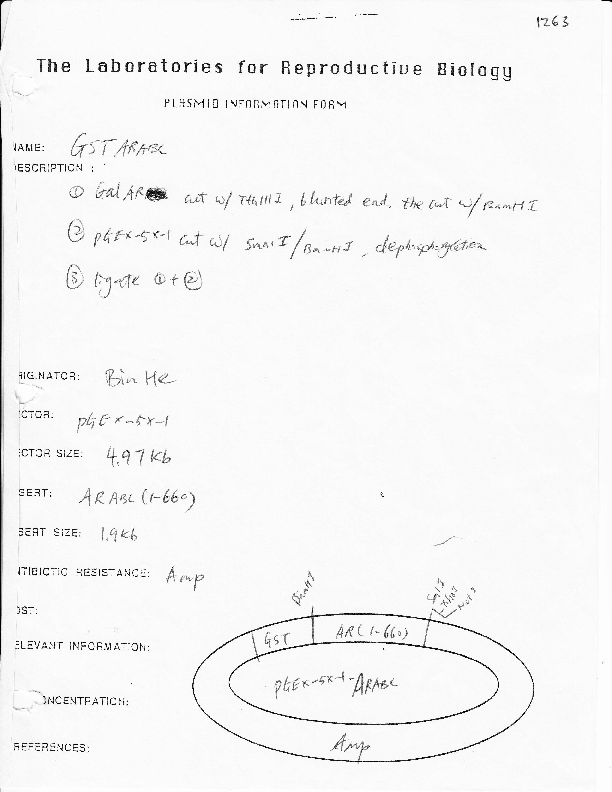
GST-AR-1-660
(Plasmid
#104196)
-
PurposeExpresses human AR-1-660 from bacterial expression vector pGEX-5X-1 as GST fusion protein
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 104196 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepGEX-5x-1
-
Backbone manufacturerPharmacia
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4970
- Total vector size (bp) 6870
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)XL-1 blue
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namehuman androgen receptor aa 1-660
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1900
-
GenBank IDAAA51886.1
-
Entrez GeneAR (a.k.a. AIS, AR8, DHTR, HUMARA, HYSP1, KD, NR3C4, SBMA, SMAX1, TFM)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- GST (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamH1 (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer don't have
- 3′ sequencing primer don't have (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The GST-AR insertion contains an insertion of 4 glutamine residues after amino acid 74 and a deletion of 4 glycine residues after amino acid 469 compared to the listed reference sequence. The depositor has confirmed that this should not affect plasmid function.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
GST-AR-1-660 was a gift from Elizabeth Wilson (Addgene plasmid # 104196 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:104196 ; RRID:Addgene_104196) -
For your References section:
FXXLF and WXXLF sequences mediate the NH2-terminal interaction with the ligand binding domain of the androgen receptor. He B, Kemppainen JA, Wilson EM. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 28;275(30):22986-94. 10.1074/jbc.M002807200 PubMed 10816582