COVID-19 and Coronavirus Plasmids & Resources
- Antibodies
- SARS-CoV-2 Plasmids
- Other Coronavirus Plasmids
- Mammalian Targets
- General Plasmid Tools
- Pooled Libraries
- Other Resources
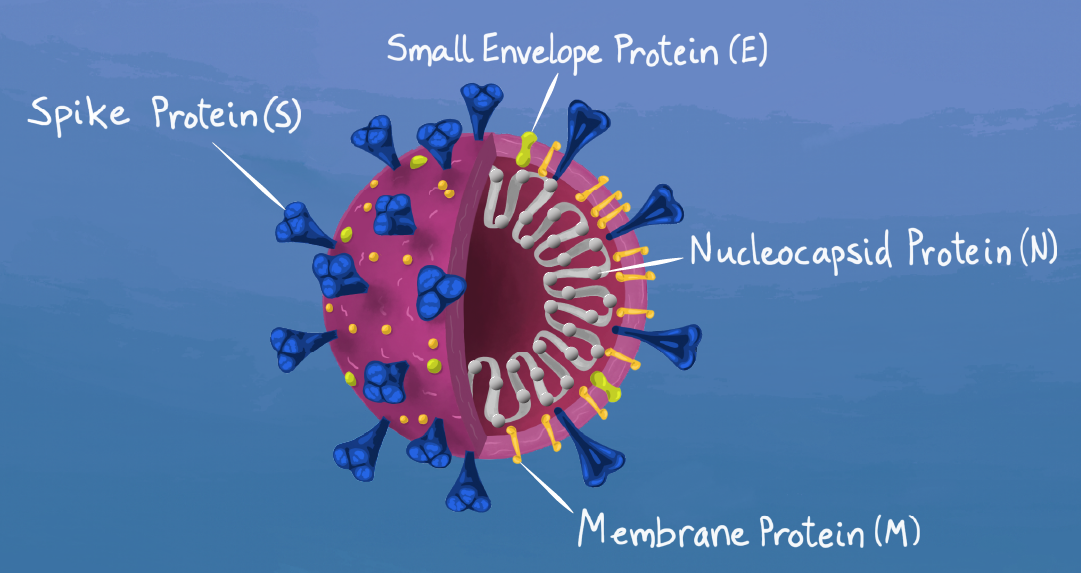
The Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic was caused by a novel virus strain from the Coronaviridae family called SARS-CoV-2. In 2020, scientists worked at lightning speed to elucidate as much as they could about this novel virus. SARS-CoV-2 entry into a host cell, like that of SARS-CoV and MERS CoV, depends on binding of the viral spike (S) protein to cellular receptors. The cellular receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV is the angiotensin receptor, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2). Another key step is the priming of the S protein by host cell proteases. The S protein of SARS-CoV-2 is primed by the serine protease TMPRSS2.
The global research community moved quickly to expand the knowledge and understanding of COVID-19 and related coronaviruses. Addgene assisted this effort by providing a platform for the distribution of plasmid-based tools that are useful for COVID-19 related research. Additionally, we have linked to collections of open-access articles, protocols, and other resource collections related to COVID-19 that may be of use to scientists.
Antibodies
| ID | Recombinant Antibody | Description | PI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 211756 | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein [mBG17] | Clone mBG17, recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody targeting the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. | Brian Geiss |
| 211757 | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein [mBG86] | Clone mBG86, recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody targeting the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. | Brian Geiss |
Plasmids
SARS-CoV-2 Plasmids
Browse the tables below to find popular plasmids expressing genes encoding SARS-CoV-2 proteins, (spike protein, S; small envelope protein, E; nucleocapsid protein, N; and membrane protein, M), including plasmids for protein production, secretion, and codon-optimized versions designed for your expression system. Some of the following plasmids are available to industry, in addition to academics and nonprofits, and this is denoted in the industry column below. For more information on ordering from a for-profit entity, please see our Plasmid Distribution to Industry page.
| ID | Plasmid | Description | Industry | PI |
|---|
Additional Addgene resources
- SARS-CoV-2 Viral Pseudotyping Collection – This page includes a table of all spike expression plasmids in our collection that are suitable for generating SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus. It also lists several luciferase and fluorescent reporter plasmids that have been used for measuring viral entry and activity in neutralization assays and links to popular envelope and packaging plasmids.
- Ginkgo Bioworks Plasmid Collection – Addgene partnered with Ginkgo Bioworks to distribute SARS-CoV-2 plasmids for E. coli, yeast, and mammalian expression, and spike protein constructs for making VSV pseudo virus.
Addgene blog
Other Coronavirus Plasmids: SARS-CoV, MERS, BAT-CoV Plasmids
| ID | Plasmid | Description | Industry | PI |
|---|
Due to export control regulations, MERS and SARS-CoV materials are available only in the US at this time.
Plasmids Encoding Mammalian Genes or Inserts
Several mammalian genes have been identified as having a key role in coronavirus infection, such as ACE2 and TMPRSS2, which are involved in the entry of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Find plasmids related to these genes below.
| ID | Plasmid | Description | Industry | PI |
|---|
Additional Addgene resources
- ACE2 plasmids - Host cell receptor mediating the entry of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 viruses (Anderson et al., 2020).
- TMPRSS2 plasmids - a serine protease that primes the SARS-CoV-2 S protein and is involved in virus entry into cells (Hoffman et al., 2020).
- FURIN plasmids - an enzyme that cleaves precursor proteins to a biologically active state. The SARS-CoV-2 S protein contains a potential cleavage site for furin proteases (Anderson et al., 2020).
- BSG plasmids - (CD147), transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily, binds to the SARS-CoV-2 S protein and is involved in virus entry into cells (Wang et al., 2020).
- Cathepsin L plasmids - a cysteine endosomal protease that triggers proteolysis of SARS-CoV Spike protein, activating its membrane fusion function (Bosch et al., 2008).
- TACE plasmids - (ADAM17) a metalloprotease that cleaves hACE2, potentially increasing viral infectivity (Heurich et al., 2014).
- PCP4 plasmids - (Purkinje cell protein 4) is involved in beating of airway cilia (Kogiso et al., 2020)
- Cytokines - SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a cytokine storm response in the body. For a full list of cytokines and related plasmids see our Immunology Resource Guide.
General Plasmid Tools
Browse the table below to find plasmid tools that may be helpful for COVID-19 research, including:
- CRISPR tools, like Cas12a and Cas13a plasmids, to reliably detect nucleic acids
- SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) activity reporters
- Reverse transcriptase, protease, and polymerase constructs for SARS-CoV-2 detection assays
- Neutralizing nanobody plasmids
- And more!
| ID | Plasmid | Description | Industry | PI |
|---|
Addgene blog
Pooled Libraries
| Pooled Library Name | Type | PI | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) Ectodomain and RBD Libraries | Screening | Timothy Whitehead | Libraries of Spike (S) Ectodomain and RBD mutants. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor Binding Domain Deep Mutation Scanning Library | Screening | Jesse Bloom | Library of Spike protein RBD mutations for comprehensive mapping. |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor Binding Domain Site-Saturation Mutagenesis Libraries | Screening |
Jesse Bloom
Tyler Starr |
Libraries of variant Spike protein RBD mutations for comprehensive mapping. |
Other Resources
Protocols
- Coronavirus Method Development Community at Protocols.io (Link opens in a new window)
- For rapid detection of the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 using CRISPR diagnostics:
- Addgene's Protocol for RNA Extraction Without A Kit
- Bloom lab - Protocol and Reagents for Pseudotyping Lentiviral Particles with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
- Nemazee lab - Pseudotyped virus protocol for coronaviruses (DOCX, 184 KB)
Research Articles
Many publishers allow free access to articles related to SARS-CoV-2 research:
- Cell Press Coronavirus Resource Hub(Link opens in a new window)
- COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 preprints from medRxiv and bioRxiv(Link opens in a new window)
- Elsevier's Novel Coronavirus Information Center(Link opens in a new window)
- The Lancet COVID-19 Resource Centre(Link opens in a new window)
- The New England Journal of Medicine Coronavirus webpage(Link opens in a new window)
- PLOS Journals COVID-19 Collection(Link opens in a new window)
- Science Journals Coronavirus Collection(Link opens in a new window)
- Springer Nature SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 Articles(Link opens in a new window)
- Wiley Online Library - Covid-19: Novel Coronavirus Content Free to Access(Link opens in a new window)
- ASM COVID-19 Research Registry(Link opens in a new window)
- COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19)(Link opens in a new window)
- LitCovid (NCBI/PubMed)(Link opens in a new window)
References
Andersen, K. G., Rambaut, A., Lipkin, W. I., Holmes, E. C., & Garry, R. F. (2020). The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nature medicine, 26(4), 450–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9 (Link opens in a new window)PMID: 32284615 (Link opens in a new window)
Bosch, B. J., Bartelink, W., & Rottier, P. J. (2008). Cathepsin L functionally cleaves the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus class I fusion protein upstream of rather than adjacent to the fusion peptide. Journal of virology, 82(17), 8887–8890. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00415-08 (Link opens in a new window)PMID: 18562523 (Link opens in a new window)
Heurich, A., Hofmann-Winkler, H., Gierer, S., Liepold, T., Jahn, O., & Pöhlmann, S. (2014). TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. Journal of virology, 88(2), 1293–1307. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02202-13 (Link opens in a new window)PMID: 24227843 (Link opens in a new window)
Hoffmann, M., Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Krüger, N., Herrler, T., Erichsen, S., Schiergens, T. S., Herrler, G., Wu, N. H., Nitsche, A., Müller, M. A., Drosten, C., & Pöhlmann, S. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell, 181(2), 271–280.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052 (Link opens in a new window)PMID: 32142651 (Link opens in a new window)
Kogiso, H., Raveau, M., Yamakawa, K., Saito, D., Ikeuchi, Y., Okazaki, T., Asano, S., Inui, T., Marunaka, Y., & Nakahari, T. (2020). Airway Ciliary Beating Affected by the Pcp4 Dose-Dependent [Ca2+]i Increase in Down Syndrome Mice, Ts1Rhr. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(6), 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21061947 (Link opens in a new window)PMID: 32178446 (Link opens in a new window)
Wang, K., Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Deng, Y., Lian, J. Q., Du, P., Wei, D., Zhang, Y., Sun, X. X., Gong, L., Yang, X., He, L., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Geng, J. J., Chen, R., Zhang, H., Wang, B., Zhu, Y. M., Nan, G., Jiang, J.L., Li, L., Wu, J., Lin, P., Huang, W., Xie, L., Zhe, Z.H., Zhang, K., Miao, J.L., Cui, H.Y., Huang, M., Zhang, J., Fu, L., Yang, X.M., Zhao, Z., Sun, S., Gu, H., Wang, Z., Wang, C.F., Lu, Y., Liu, Y.Y., Wang, Q.Y., Bian, H., Zhu, P., Chen, Z. N. (2020). CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 5(1), 283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x (Link opens in a new window) PMID: 33277466 (Link opens in a new window)
Content last reviewed on 26 September 2025.
Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!



