 Ras Pathway
Ras Pathway
Background
Ras is a small GTPase and is a member of the G protein (guanine nucleotide binding protein) family. GTPases serve as molecular switches that transmit signals within the cell. GTPases have an active (GTP) and inactive (GDP) state, regulated by the addition and removal of a phosphate group. Under normal physiological conditions GTPases play prominent roles in signaling pathways regulating cell migration, survival, adhesion, growth, and differentiation.

Cancer Impact
Ras is ubiquitously expressed in all cells and all tissues. Ras can activate a variety of pathways, which ultimately turn on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and survival. Ras is essential for regulating the growth of the cell, however when mutations occur in the Ras gene it can be stuck in a constitutively active form, constantly activating pathways for cell growth and potentially leading to cancer. Constitutively active Ras is the most common oncogene in human cancer, found in around 20-25% of all human cancers.
Ras Pathway Plasmids
Click on a name to find available plasmids for the gene, or browse the gene list below. For proteins with multiple subunits or isoforms, individual links to each gene page are provided below. Color is used for clarity and does not indicate a specific relationship.
The content and map for this page were generated with the help of Dominic Esposito and the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research .
Color is used for clarity and does not indicate a specific relationship.
The content and map for this page were generated with the help of Dominic Esposito and the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research .
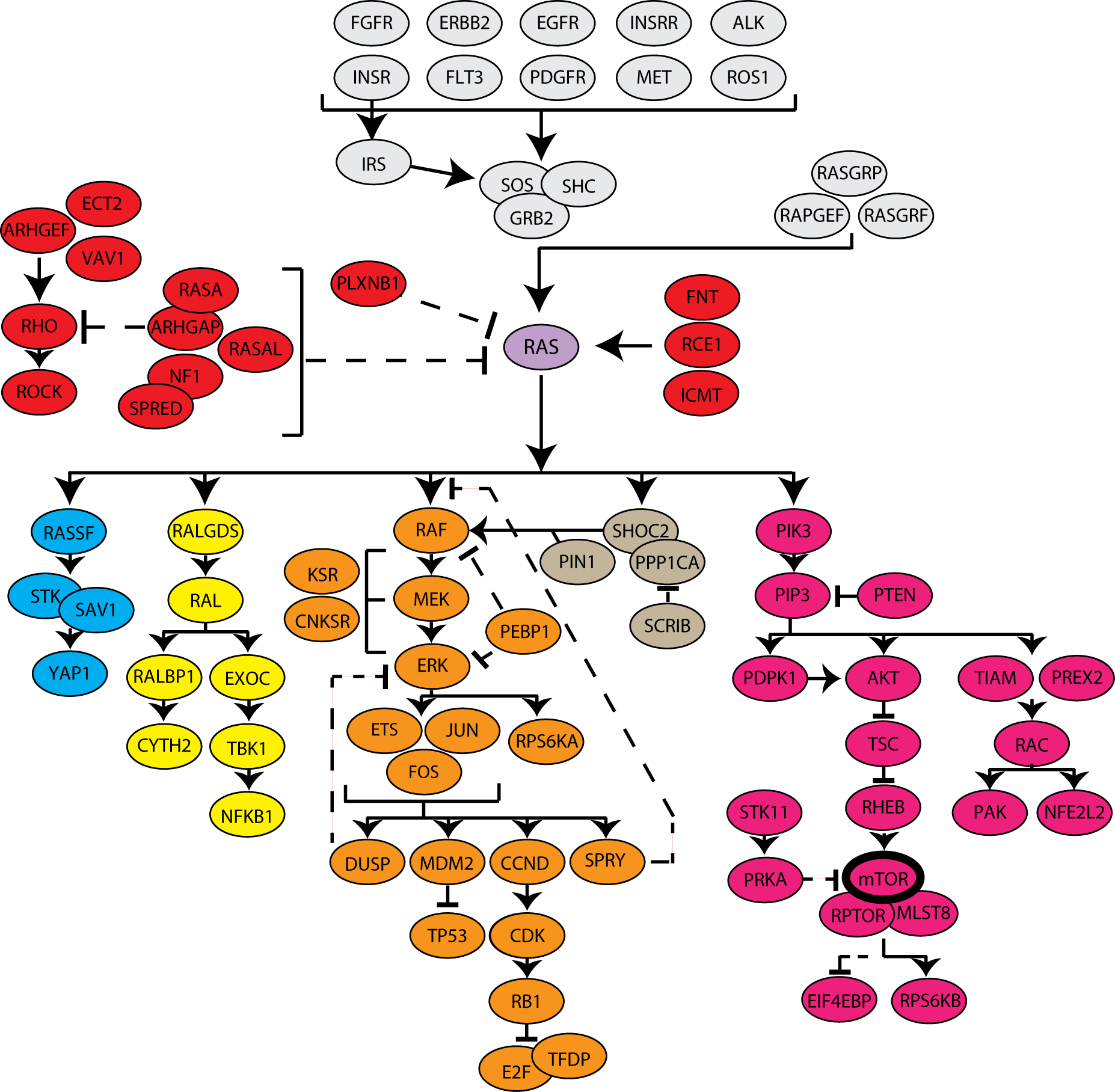
Ras Pathway - Gene List
Click on a name to find available plasmids for the gene. For components with multiple subunits or isoforms, individual links to each gene page are provided below.
| Symbol | Name |
|---|---|
| AKT | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3 |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ARHGAP35 | Rho GTPase activating protein 35 |
| ARHGEF2 | Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
| CCND | Cyclin D |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CNKSR | Connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of Ras |
| CYTH2 | Cytohesin 2 |
| DUSP | Dual specificity phosphatase |
| E2F | E2F transcription factor |
| ECT2 | Epithelial cell transforming 2 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EIF4EBP | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein |
| ERBB2 | Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| ERK | Also known as MAPK; Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ETS | ETS proto-oncogene, transcription factor |
| EXOC | Exocyst complex component |
| FGFR | Fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| FLT3 | Fms related tyrosine kinase 3 |
| FNT | Farnesyltransferase, CAAX box |
| FOS | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| GRB2 | Growth factor receptor bound protein 2 |
| ICMT | Isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase |
| INSR | Insulin receptor |
| INSRR | Insulin receptor-related receptor |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| JUN | Jun proto-oncogene |
| KSR | Kinase suppressor of ras |
| MDM2 | MDM2 proto-oncogene |
| MEK | Also known as MAP2K; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| MET | MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| MLST8 | MTOR associated protein, LST8 homolog |
| MTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NF1 | Neurofibromin 1 |
| NFE2L2 | Nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 |
| NFKB1 | Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
| PAK | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase |
| PDGFR | Platelet derived growth factor receptor |
| PDPK1 | 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase 1 |
| PEBP1 | Phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 1 |
| PIK3 | Also known as PI3K; Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic and regulatory subunits - Class I |
| PIN1 | Peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 |
| PLXNB1 | Plexin B1 |
| PPP1CA | Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha |
| PREX2 | Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 2 |
| PRKA |
Protein kinase AMP-activated:
A1,A2: Catalytic subunit alpha B1,B2: non-catalytic subunit beta G1, G2, G3: non-catalytic subunit gamma |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| RAC | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac) |
| RAF |
Serine/threonine kinases:
A-Raf proto-oncogene B-Raf proto-oncogene Raf-1 proto-oncogene |
| RAL | v-ral simian leukemia viral oncogene homolog (ras related) |
| RALBP1 | RalA binding protein 1 |
| RALGDS | Ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator |
| RAPGEF | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| RAS |
Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog Muscle RAS oncogene homolog Neuroblastoma RAS viral (v-ras) oncogene homolog |
| RASA | RAS p21 protein activator |
| RASAL | RAS protein activator like |
| RASGRF | Ras protein specific guanine nucleotide releasing factor |
| RASGRP | RAS guanyl releasing protein |
| RASSF | Ras association domain family member |
| RB1 | Retinoblastoma 1 |
| RCE1 | Ras converting CAAX endopeptidase 1 |
| RHEB | Ras homolog enriched in brain |
| RHO | Ras homolog family member |
| ROCK | Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase |
| ROS1 | ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| RPS6KA | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase |
| RPS6KB | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase B1 |
| RPTOR | Regulatory associated protein of MTOR, complex 1 |
| SAV1 | Salvador family WW domain containing protein 1 |
| SCRIB | Scribbled planar cell polarity protein |
| SHC | SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein |
| SHOC2 | SHOC2 leucine-rich repeat scaffold protein |
| SOS | SOS Ras/Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| SPRED | Sprouty related, EVH1 domain containing |
| SPRY | Sprouty RTK signaling antagonist |
| STK | Serine/threonine kinase |
| STK11 | Serine/threonine kinase 11 |
| TBK1 | TANK binding kinase 1 |
| TFDP | Transcription factor Dp |
| TIAM | T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| TSC | Tuberous sclerosis |
| VAV1 | Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 |
| YAP1 | Yes associated protein 1 |
Resources
RAS Pathway Clone Collection 2.0:Set of vectors from the Esposito Lab for use with the Gateway® Cloning Platform (Life Technologies™) to permit construction of RAS pathway gene expression vectors for in vitro and in vivo research.
The RAS Initiative- at the National Cancer Institute (NCI)
References
Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR, Albert S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1773(8):1177-95. PubMed PMID: 17428555 .
RAS signaling pathways, mutations and their role in colorectal cancer. Zenonos K, Kyprianou K. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2013 May 15; 5(5): 97–101. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i5.97. PubMed PMID: 23799159 .
Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Downward J. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003 Jan;3(1):11-22. PubMed PMID: 12509763 .
Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!



