 mTOR Pathway
mTOR Pathway
The mechanistic or mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key metabolic regulator controlling cell growth and proliferation. mTOR, a serine/threonine kinase, is found in two complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. Each complex contains a unique subunit: raptor for mTORC1, and rictor for mTORC2.
Background
mTORC1 & mTORC2
The better-characterized mTORC1 responds to various signals, including amino acids, stress, oxygen, energy levels, and growth factors. mTORC1 integrates these signals to determine the nutritional state of the cell and regulates the switch from anabolic to catabolic processes. Active mTORC1 promotes protein and lipid synthesis, and increases energy production through glycolysis to fuel these energy-intensive processes. mTORC1 also blocks catabolic processes including autophagy and lysosome biogenesis.
mTORC2 does not respond to nutrients, but it is activated by growth factors, including insulin. mTORC2 influences cell survival and cytoskeletal organization.
Cancer Impact
Enhanced signaling through either mTORC1 or mTORC2 correlates with poor prognosis in many cancers, including breast, colon, ovarian, and liver cancers. mTORC1 is activated downstream of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK, both of which are commonly dysregulated in cancer. Loss of the tumor suppressor p53 also promotes aberrant mTORC1 activity, and multiple familial cancers are caused by inactivating mutations in negative regulators of mTORC1. The hyperactivation of mTORC1 in cancer promotes the conditions needed for uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation, including an abundant supply of macromolecules and energy, as well as the presence of both pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic signals. mTORC2, which appears to signal upstream of Akt, also promotes cell survival and proliferation.
mTOR Pathway Plasmids
Click on a name to find available plasmids for the gene, or browse the gene list below. For multiple isoforms or subunits, individual links to each gene page are provided below. Color is used for clarity and does not indicate a specific relationship.
The content for this page was generated with the help of David Sabatini .
mTOR Pathway
Color is used for clarity and does not indicate a specific relationship.
The content for this page was generated with the help of David Sabatini .
mTOR Pathway - Gene List
Click on a name to find available plasmids for the gene. For components with multiple isoforms or subunits, individual links to each gene page are provided below.
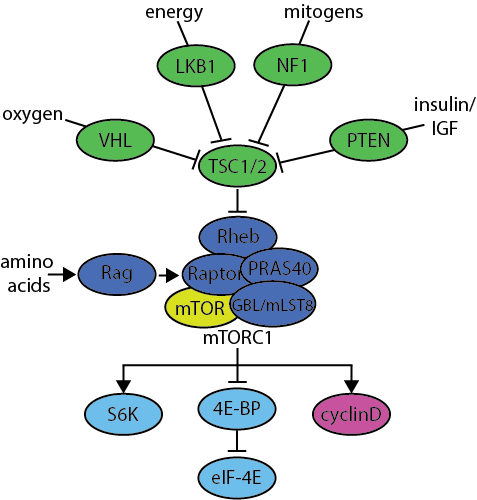
mTORC1 Complex
| Symbol | Name |
|---|---|
| 4E-BP | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, binding protein 1 |
| Cyclin D1 | Also known as CCND1 |
| eIF-4E | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E |
| GBL/mLST8 | MTOR associated protein; LST8 homolog |
| LKB1 | Also known as STK11; serine/threonine kinase 11 |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NF1 | Neurofibromin 1 |
| PRAS40 | Also known as AKT1S1; AKT1 substrate 1 (proline rich) |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Rag | Ras-related GTP binding |
| Raptor | Also known as RPTOR; Regulatory associated protein of MTOR, complex 1 |
| Rheb | Ras homolog enriched in brain |
| S6K | Also known as RPS6KB1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase B1 |
| TSC1/2 | Tuberous sclerosis |
| VHL | Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor |
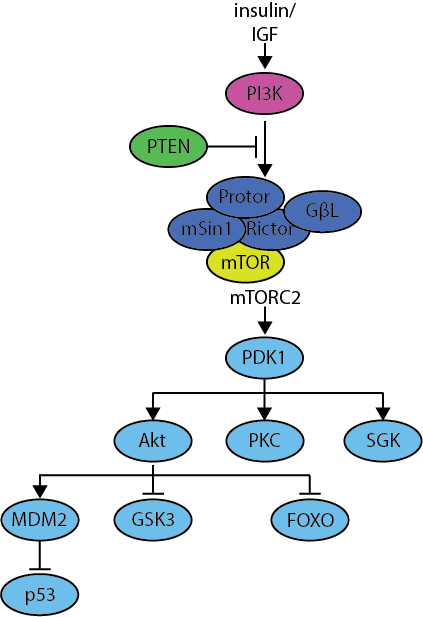
mTORC2 Complex
| Symbol | Name |
|---|---|
| AKT | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog |
| FOXO | Forkhead box O |
| GBL/mLST8 | MTOR associated protein; LST8 homolog |
| GSK3 | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| MDM2 | MDM2 proto-oncogene |
| mSin1 | Also known as MAPKAP1; Mitogen-activated protein kinase associated protein 1 |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| p53 | TP53; tumor protein p53 |
| PDK1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic and regulatory subunits - Class I |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| Protor | Also known as PRR5; proline rich 5 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Rictor | RPTOR independent companion of MTOR, complex 2 |
| SGK | Serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 |
Resources
Cancer Pathway ORF Kit(Sabatini & Wood)
Tackling Cancers’ Drug Resistance with a New Screening Kit(from David Sabatini & Kris Wood)
References
mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Laplante M, Sabatini DM. Cell. 2012 Apr 13;149(2):274-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. PubMed PMID: 22500797 .
Rapamycin: one drug, many effects. Li J, Kim SG, Blenis J. Cell Metab. 2014 Mar 4;19(3):373-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.001. PubMed PMID: 24508508 .
Targeting the translation machinery in cancer. Bhat M, Robichaud N, Hulea L, Sonenberg N, Pelletier J, Topisirovic I. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Apr;14(4):261-78. doi: 10.1038/nrd4505. PubMed PMID: 25743081 .

Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!
