RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9-based transcription factors.
Perez-Pinera P, Kocak DD, Vockley CM, Adler AF, Kabadi AM, Polstein LR, Thakore PI, Glass KA, Ousterout DG, Leong KW, Guilak F, Crawford GE, Reddy TE, Gersbach CA
Nat Methods. 2013 Jul 25. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2600.
(Link opens in a new window)
PubMed
(Link opens in a new window)
Article
These mammalian expression plasmids encode the nuclease-null dCas9 (D10A, H840A) with HA and FLAG epitope tags either alone or fused to the transcriptional activator VP64. When directed to its target in gene promoters by the sgRNA expressed in trans from pSPgRNA, the dCas9-VP64 fusion protein activates the expression of downstream genes. Multiple sgRNAs targeted to the same promoter act synergistically to activate gene expression. The dCas9 protein serves as a negative control of the function of the VP64 activator and can also be used to inhibited gene expression via steric hindrance.
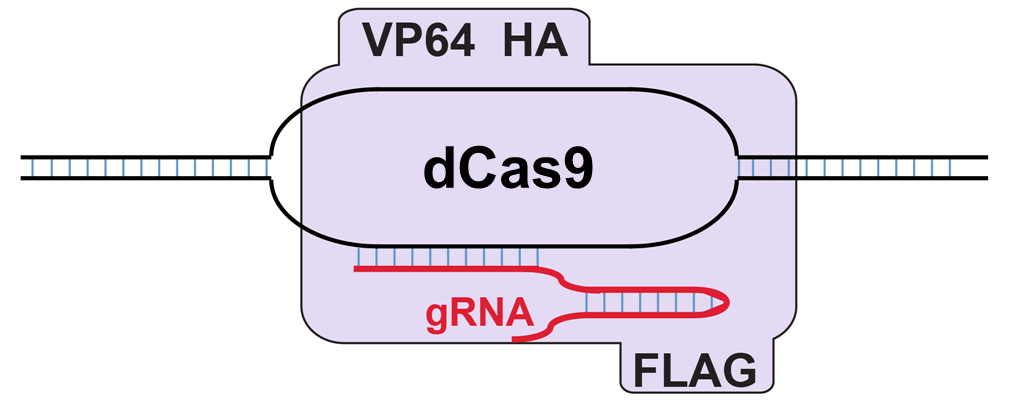
Figure 1: The dCas9-VP64 fusion protein activates the expression of downstream genes.
Plasmids from Article
| ID | Plasmid | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 47106 | pcDNA-dCas9 | Expresses inactivated S. pyogenes dCas9 (D10A, H840A) in mammalian cells |
| 47107 | pcDNA-dCas9-VP64 | Expresses inactivated S. pyogenes dCas9 (D10A, H840A) fused to VP64 transactivator domain in mammalian cells |
| 47108 | pSPgRNA | Expresses a S. pyogenes Cas9/dCas9 guide RNA in mammalian cells |
