-
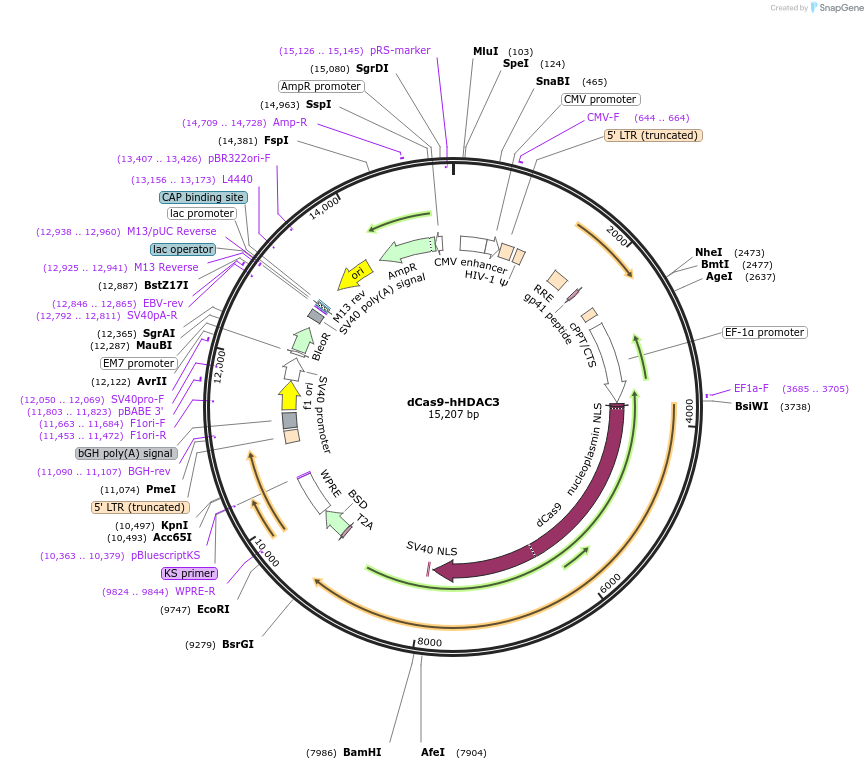
Purpose3rd generation lenti vector encoding dCas9-hHDAC3 (EF1a-NLS-dCas9(N863)-hHDAC3). Expresses dCas9 fused to human HDAC3.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 98591 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneplenti
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Lentiviral, CRISPR
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namedCAS9-HDAC3
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human), Synthetic; S. pyogenes
-
MutationD10A and N863A in Cas9
-
GenBank IDNM_003883
-
Entrez GeneHDAC3 (a.k.a. HD3, KDAC3, RPD3, RPD3-2)
- Promoter EF1A
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer GTTTGGATCTTGGTTCATTCTCAAGCCTCAG
- 3′ sequencing primer cacatagcgtaaaaggagcaacatag
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byhuman HDAC3 cDNA from Addgene plasmid HDAC3-Flag (#13819) plenti vector containing dCas9_2A_Blast from Addgene plasmid (#61425)
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The stop codon present after the HDAC3 open reading frame may interfere with expression of the blasticidin resistance cassette. Blasticidin selection has not been verified with this plasmid.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
dCas9-hHDAC3 was a gift from Zhaolan Zhou (Addgene plasmid # 98591 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:98591 ; RRID:Addgene_98591) -
For your References section:
Locus-specific histone deacetylation using a synthetic CRISPR-Cas9-based HDAC. Kwon DY, Zhao YT, Lamonica JM, Zhou Z. Nat Commun. 2017 May 12;8:15315. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15315. 10.1038/ncomms15315 PubMed 28497787