-
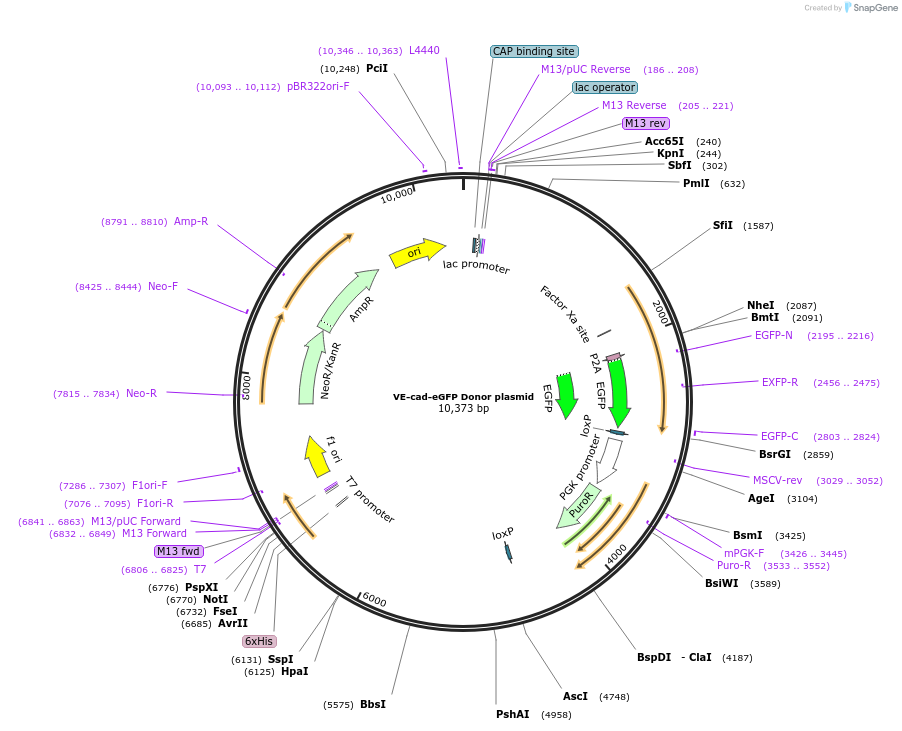
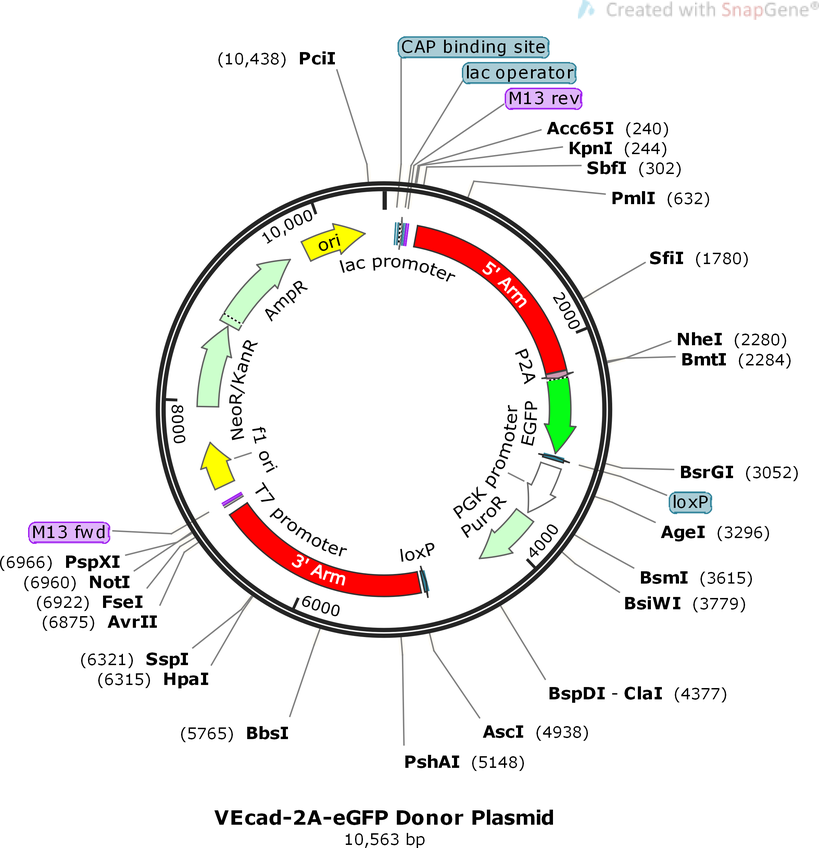
PurposeKnock eGFP into human VE-cad locus
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 92309 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneOct4-2A-eGFP backbone
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 8563
- Total vector size (bp) 10438
-
Modifications to backboneLeft and right arms of Oct4 were replaced with VEcad arms
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, CRISPR
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameVEcad Homologous Recombination Arms
-
Alt nameCDH5
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)2000
-
Mutationabout 30 a.a. truncated at end of protein
-
GenBank ID1003
-
Entrez GeneCDH5 (a.k.a. 7B4, CD144)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SbfI, AscI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NheI, FseI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer M13 RVS
- 3′ sequencing primer M13 FWD (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
This plasmid functions as described in the related publication, but the 5' homology arm is 528bp instead of ~2kbp.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
VE-cad-eGFP Donor plasmid was a gift from Sean Palecek (Addgene plasmid # 92309 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:92309 ; RRID:Addgene_92309) -
For your References section:
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived epicardial progenitors can differentiate to endocardial-like endothelial cells. Bao X, Bhute VJ, Han T, Qian T, Lian X, Palecek SP. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017 Jun;2(2):191-201. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10062. Epub 2017 May 22. 10.1002/btm2.10062 PubMed 29170757