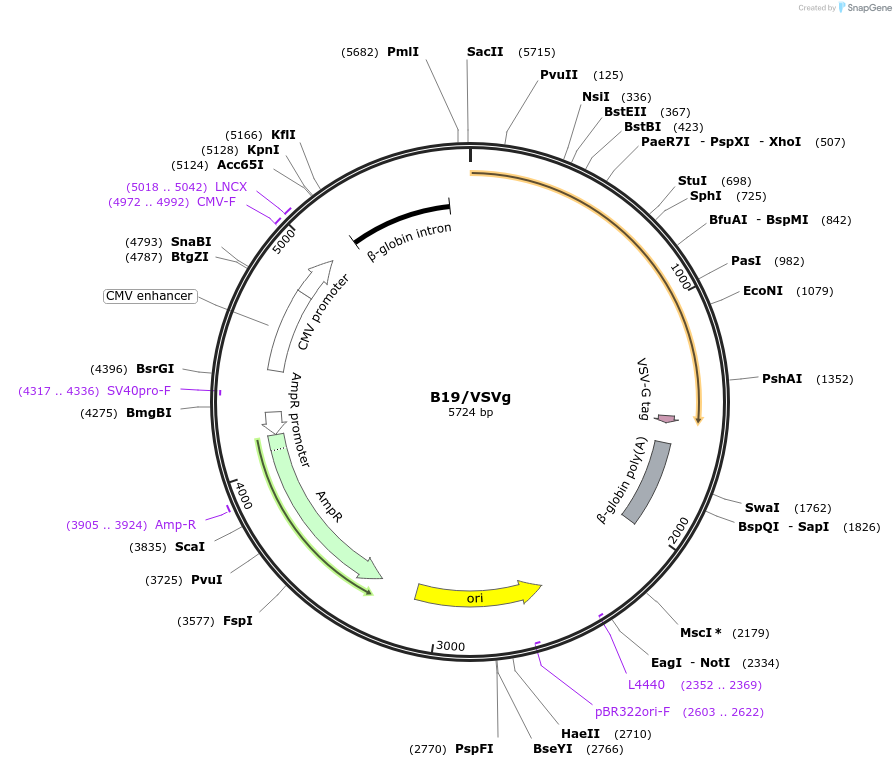
B19/VSVg
(Plasmid
#88865)
-
Purposeenvelope pseudotyping of lentiviral vectors
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 88865 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepLP
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameVSVg-B19 chimera
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
B19 cloned from Addgene 15785. VSVG subcloned from Invitrogen virapower
Addgene sequencing found I474V within the G protein translation; however depositor confirms that this makes no difference to protein function and is the same construct as published in the manuscript Schoderboeck et al. 2015.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
B19/VSVg was a gift from Stephanie Hughes (Addgene plasmid # 88865) -
For your References section:
Chimeric rabies SADB19-VSVg-pseudotyped lentiviral vectors mediate long-range retrograde transduction from the mouse spinal cord. Schoderboeck L, Riad S, Bokor AM, Wicky HE, Strauss M, Bostina M, Oswald MJ, Empson RM, Hughes SM. Gene Ther. 2015 May;22(5):357-64. doi: 10.1038/gt.2015.3. Epub 2015 Jan 29. 10.1038/gt.2015.3 PubMed 25630949