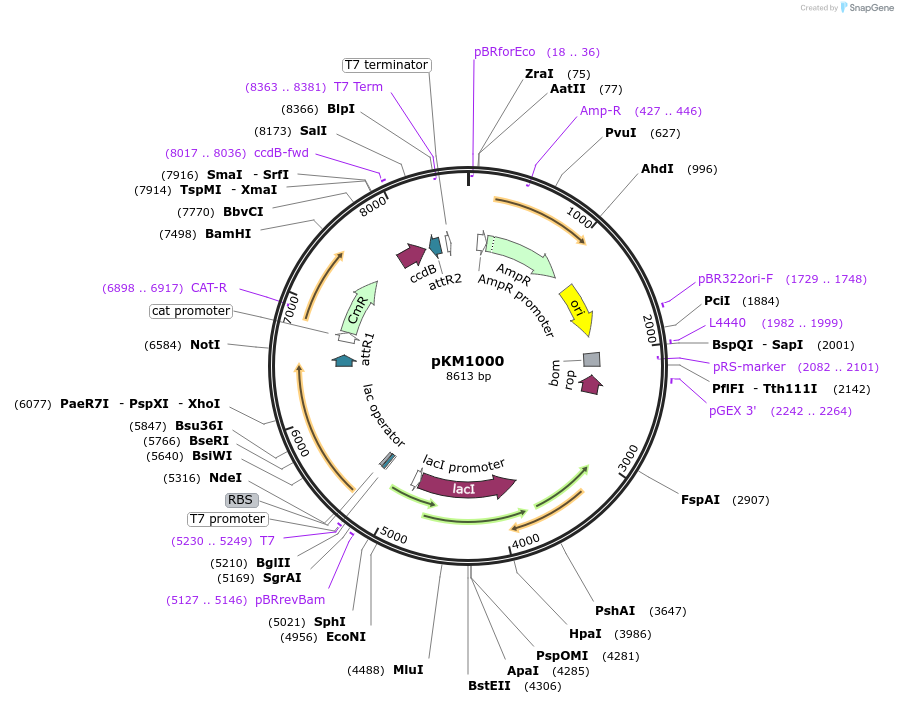
pKM1000
(Plasmid
#8840)
-
Purpose(Empty Backbone)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 8840 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepET11
-
Backbone manufacturerNovagen
- Backbone size (bp) 6700
-
Modifications to backboneDNA encoding presumptive N-terminal signal peptide deleted. The single cysteine in T. maritima MBP (residue 12) was changed to a serine by site-directed mutagenesis.
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- T. maritima MBP (N terminal on backbone)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Chloramphenicol and Ampicillin, 25 & 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)ccdB Survival
-
Growth instructionsBecause it carries a gene (ccdB ) that encodes a lethal DNA gyrase poison, this vector must be propogated in an E. coli gyrA mutant such as DB3 or DB5 (Invitrogen), which is immune to the action of CcdB.
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gateway Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer pBRrevBam; T7
- 3′ sequencing primer T7term
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
A Gateway destination vector for the production of recombinant proteins as fusions to the C-terminus of T. maritima maltose-binding protein. DNA encoding presumptive N-terminal signal peptide deleted. The single cysteine in T. maritima MBP (residue 12) was changed to a serine by site-directed mutagenesis.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pKM1000 was a gift from David Waugh (Addgene plasmid # 8840 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:8840 ; RRID:Addgene_8840) -
For your References section:
Maltodextrin-binding proteins from diverse bacteria and archaea are potent solubility enhancers. Fox JD, Routzahn KM, Bucher MH, Waugh DS. FEBS Lett. 2003 Feb 27. 537(1-3):53-7. 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00070-X PubMed 12606030