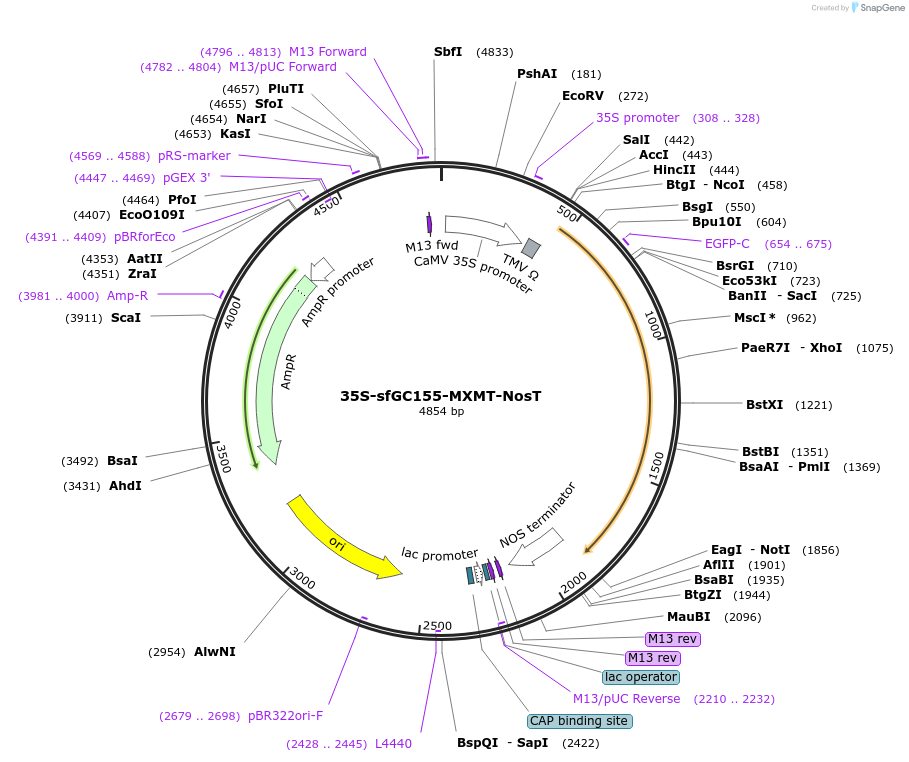
35S-sfGC155-MXMT-NosT
(Plasmid
#80166)
-
PurposeBiFC vector for transient expression of sfGC155-MXMT in plants
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 80166 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBRN169-MXMT
-
Backbone manufacturerKodama and Wada 2009
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3465
- Total vector size (bp) 4854
-
Modifications to backbonePCR-amplied DNA fragments (sfGC) for BiFC fragments were subcloned into the NcoI/BsrGI site of pBRN169-MXMT vector.
-
Vector typePlant Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namesfGFP(156-238)
-
Alt namesfGC155
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)258
- Promoter CaMV 35S promoter
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- sfGC155 (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoⅠ (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BsrGⅠ (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GGATCCATGGTGGACAAGCAGAAGAACGGC
- 3′ sequencing primer TTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGCCGAGAGT
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
35S-sfGC155-MXMT-NosT was a gift from Yutaka Kodama (Addgene plasmid # 80166 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:80166 ; RRID:Addgene_80166) -
For your References section:
In planta comparative analysis of improved green fluorescent proteins with reference to fluorescence intensity and bimolecular fluorescence complementation ability. Fujii Y, Kodama Y. Plant Biotech. 2015; 32(1): 81-87. 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.15.0120a