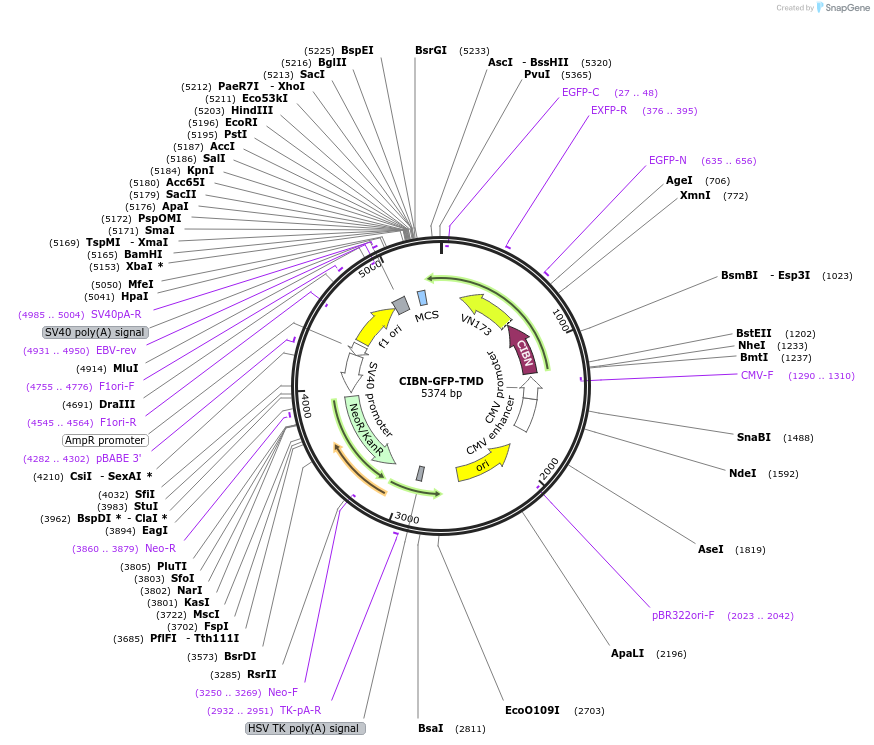
CIBN-GFP-TMD
(Plasmid
#79571)
-
Purposeexpression of CIBN domain fused to GFP tagged mouse Syntaxin1 TMD domain (transmembrane domain and polybasic region)
-
Depositing Labs
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 79571 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepEGFP
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namesyntaxin 1A
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Mutationaa 249_288 (C-terminal region (polybasic stretch and transmembrane domain from human Syntaxin 1A)
-
Entrez GeneStx1a (a.k.a. HPC-1)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- CIBN (N terminal on backbone)
- EGFP (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site PvuI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BsrG1 (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-F
- 3′ sequencing primer SV40pA-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
This plasmid contains the C-terminal region (polybasic stretch and transmembrane domain; amino acids 249-288) from human Syntaxin 1A (NM_004603.3).
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
CIBN-GFP-TMD was a gift from Pietro De Camilli & Olof Idevall-Hagren (Addgene plasmid # 79571 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:79571 ; RRID:Addgene_79571) -
For your References section:
Optogenetic control of phosphoinositide metabolism. Idevall-Hagren O, Dickson EJ, Hille B, Toomre DK, De Camilli P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 28;109(35):E2316-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211305109. Epub 2012 Jul 30. 10.1073/pnas.1211305109 PubMed 22847441