-
PurposeA fusion of zebrafish synaptophysin to GFP under the control of 5UAS repeats
-
Depositing Labs
-
Publication
-
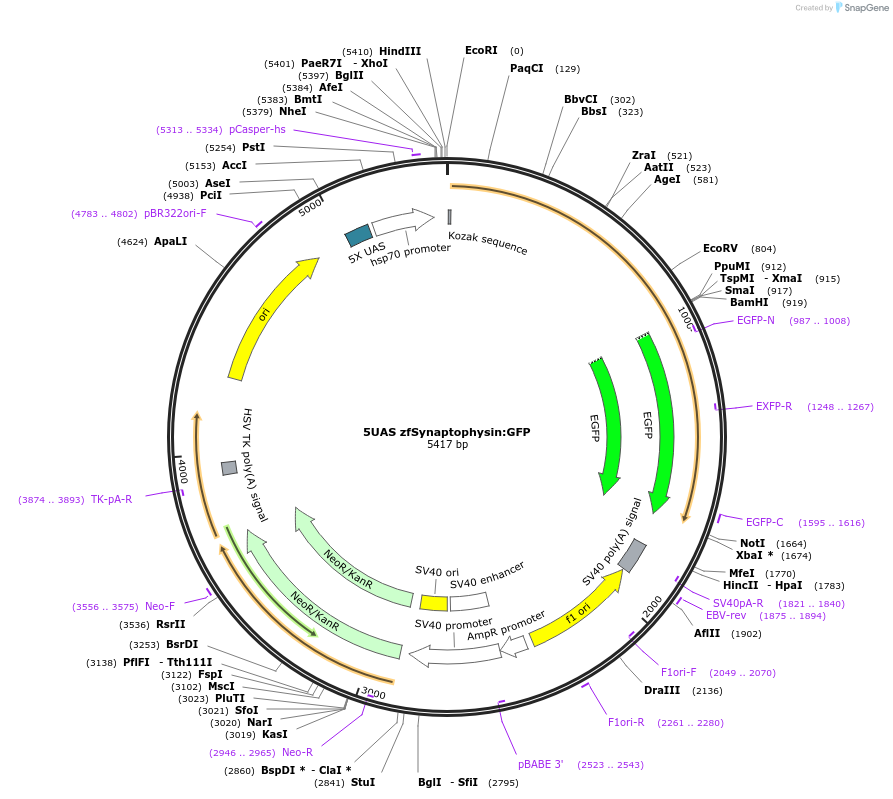
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 74316 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepEGFP-N2
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5000
- Total vector size (bp) 6000
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namesynaptophysin
-
SpeciesD. rerio (zebrafish)
-
Insert Size (bp)960
-
MutationQ12H and deletion of F13 (please see depositor comment below)
- Promoter 5UAS
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site Ecor1 (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site Sma1 (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer ATGGATGTTGCCAACCAGTT
- 3′ sequencing primer TGGACGAGCTGTACAAGTAA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The depositor noted that the Q12H mutation and deletion of F13 found in Addgene's quality control sequence does NOT affect plasmid function.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
5UAS zfSynaptophysin:GFP was a gift from Martin Meyer & Stephen Smith (Addgene plasmid # 74316 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:74316 ; RRID:Addgene_74316) -
For your References section:
Evidence from in vivo imaging that synaptogenesis guides the growth and branching of axonal arbors by two distinct mechanisms. Meyer MP, Smith SJ. J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 29;26(13):3604-14. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0223-06.2006 PubMed 16571769