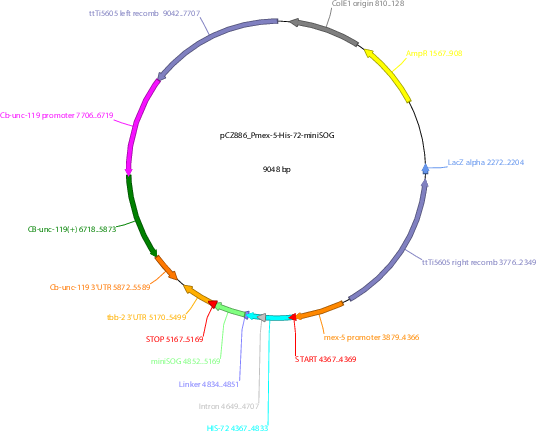
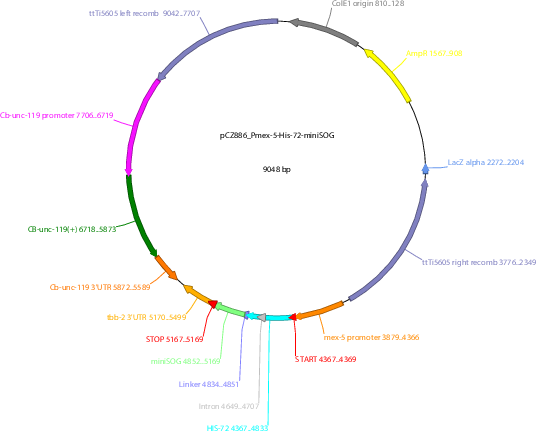
pCZ886
(Plasmid
#73584)
-
PurposePmex-5-HIS-72-miniSOG-3'UTR(tbb-2) for optogenetic mutagenesis
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 73584 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCFJ150
- Total vector size (bp) 9048
-
Vector typeWorm Expression ; For MosSCI insertion
-
Selectable markersCb-unc-119
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameHIS-72
-
Alt nameHistone 72, H3 histone
-
SpeciesC. elegans (nematode)
-
Insert Size (bp)467
-
Entrez Genehis-72 (a.k.a. CELE_Y49E10.6)
- Promoter Pmex-5
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- miniSOG (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer GCACCGTACGTCTCGAGtgtaaaacgacggccagtgtacgactcactatagggcgaattg
- 3′ sequencing primer GTACCAGAGCTCACCTAGGcaggaacagctatgacccaatgagacttttttcttggcggc (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byThe backbone is pCFJ150, made in the lab of Erik M. Jorgensen, University of Utah.
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCZ886 was a gift from Yishi Jin (Addgene plasmid # 73584 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:73584 ; RRID:Addgene_73584) -
For your References section:
Optogenetic mutagenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Noma K, Jin Y. Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 3;6:8868. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9868. 10.1038/ncomms9868 PubMed 26632265