-
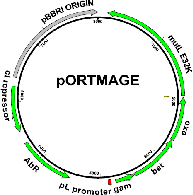
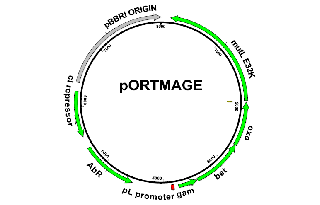
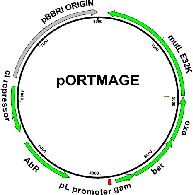
PurposeExpresses Lambda Red recombinases and a dominant negative MutL allele all controlled by temperature sensitve cI857 repressor for high precision and efficiency MAGE experiments. Kan resistance marker.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 72678 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepSIM8
-
Backbone manufacturerDatta S. et al. (Gene 379 (2006) 109-115)
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6248
- Total vector size (bp) 8096
-
Modifications to backboneMutL E32K allele cloned into vector
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Growth instructionsInduction of expression of Lambda recombinases and MutL E32K allele at 42°C for 15 minutes, otherwise grow at 30°C
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namemutL E32K
-
SpeciesEscherichia coli
-
Insert Size (bp)1848
-
MutationE32K mutation conferring dominant mutator phenotype
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- none (N terminal on insert)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please visit the depositor's website: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/sysbiol/pal-csaba-lab-resources.html for additional resource information.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pORTMAGE-3 was a gift from Csaba Pál (Addgene plasmid # 72678 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:72678 ; RRID:Addgene_72678) -
For your References section:
A highly precise and portable genome engineering method allows comparison of mutational effects across bacterial species. Nyerges A, Csorgo B, Nagy I, Balint B, Bihari P, Lazar V, Apjok G, Umenhoffer K, Bogos B, Posfai G, Pal C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 16. pii: 201520040. 10.1073/pnas.1520040113 PubMed 26884157