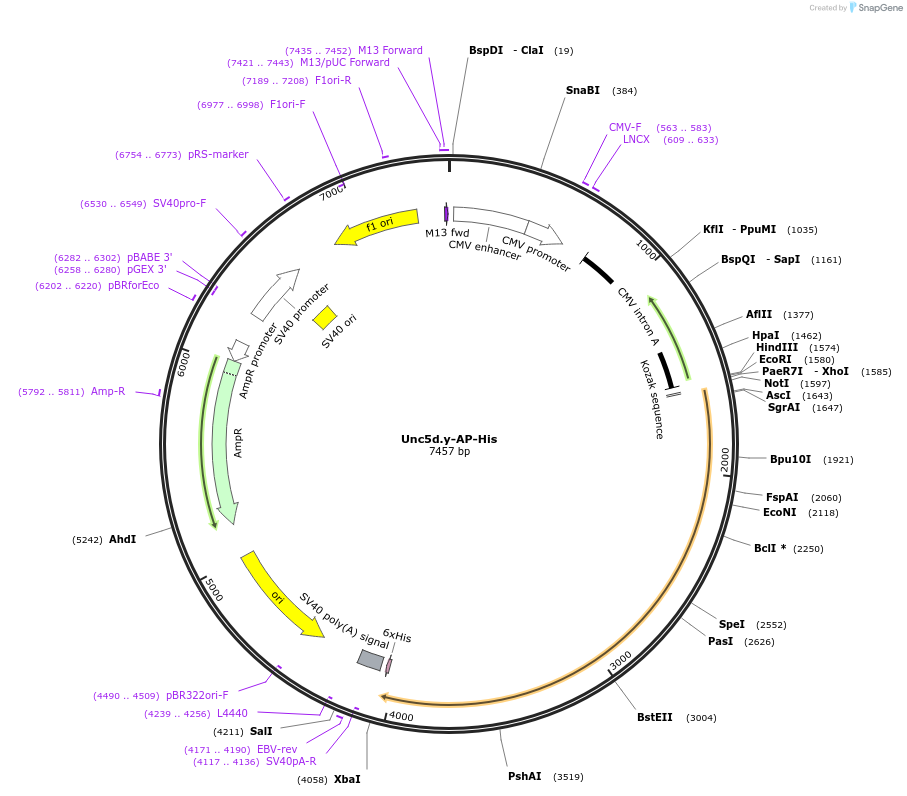
Unc5d.y-AP-His
(Plasmid
#72058)
-
PurposeExpresses the extracellular region of the Unc5D, isoform y protein, C-terminally fused to alkaline phosphatase + 6X histidine tag.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 72058 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMVi-SV40ori
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameUnc5d.y
-
Alt nameUnc5D, isoform y; Unc5h4
-
Alt nameNCBI gene ID 210801
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)942
-
Entrez GeneUnc5d (a.k.a. D930029E11Rik, Unc5h4, mKIAA1777)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- AP-His (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site SpeI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GTCAGAGGTAACTCCCGTTGC
- 3′ sequencing primer GAGGTTCTTGGCGGCTGTC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Unc5d.y is missing exons 6 and 8.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
Unc5d.y-AP-His was a gift from Woj Wojtowicz (Addgene plasmid # 72058 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:72058 ; RRID:Addgene_72058) -
For your References section:
An extracellular biochemical screen reveals that FLRTs and Unc5s mediate neuronal subtype recognition in the retina. Visser JJ, Cheng Y, Perry SC, Chastain AB, Parsa B, Masri SS, Ray TA, Kay JN, Wojtowicz WM. Elife. 2015 Dec 3;4. pii: e08149. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08149. 10.7554/eLife.08149 PubMed 26633812