-
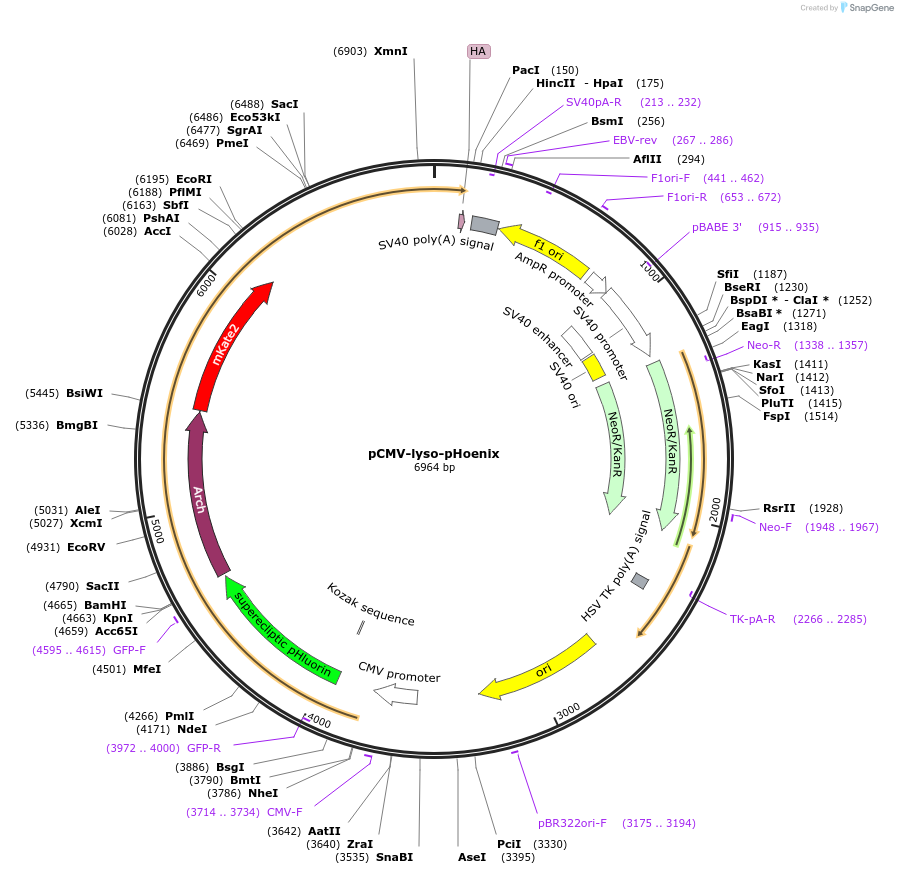
PurposeExpression of lyso-pHoenix in mammalian cells for optogenetic acidification of lysosomes
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 70112 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMV
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3878
- Total vector size (bp) 7157
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)XL10 Gold
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namelyso-pHoenix
-
Alt nameCD63-pHluorin-Arch3-mKate2-betaHK
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse), R. norvegicus (rat); Halorubrum sodomense, Entacmaea quadricolor, Aequorea victoria
-
Insert Size (bp)3492
-
GenBank ID12512; KT880225
-
Entrez GeneCd63 (a.k.a. ME491, Tspan30)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- pHluorin
- Arch3
- mKate2
- H+/K+ ATPase beta-subunit
- HA-Tag (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site PacI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG
- 3′ sequencing primer TTGTGAAATTTGTGATGCTATTGC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byArch3: Addgene Plasmid #22222; mKate2: Evrogen
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV-lyso-pHoenix was a gift from Christian Rosenmund (Addgene plasmid # 70112 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:70112 ; RRID:Addgene_70112) -
For your References section:
Optogenetic acidification of synaptic vesicles and lysosomes. Rost BR, Schneider F, Grauel MK, Wozny C, G Bentz C, Blessing A, Rosenmund T, Jentsch TJ, Schmitz D, Hegemann P, Rosenmund C. Nat Neurosci. 2015 Nov 9. doi: 10.1038/nn.4161. 10.1038/nn.4161 PubMed 26551543