-
PurposeRunx1 +23 kb intronic enhancer from mouse and beta-globin minimal promoter in a 5' entry vector for gateway cloning
-
Depositing Labs
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 69602 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
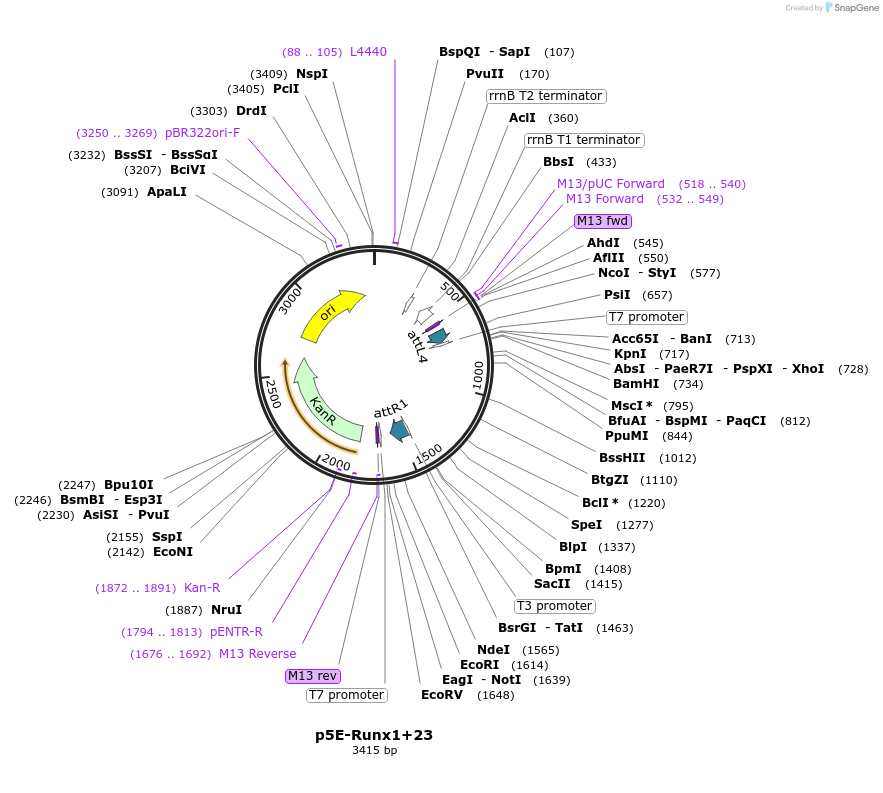
Vector backbonepENTR attL4-R1
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4777
- Total vector size (bp) 3415
-
Vector type5' Gateway Entry Vector
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert nameRunx1 +23 intronic enhancer
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)548
-
Entrez GeneRunx1 (a.k.a. AML1, CBF-alpha-2, Cbfa2, Pebp2a2, Pebpa2b)
- Promoter C57/BL6 mouse Runx1 +23 intronic enhancer
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 1
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site XhoI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BglII (destroyed during cloning)
- 5′ sequencing primer GGCTCGAGGGATCCGGGGTGGGAGGTGTAAGTTC
- 3′ sequencing primer GGGCGGCCGCAGATCTCAGGTGTCAGCAACCCATC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert nameMouse beta-globin minimal promoter
-
Alt nameProximal promoter of Mus musculus hemoglobin, beta adult minor chain
-
Alt nameHbb-bt proximal promoter
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)131
-
GenBank IDNM_008220.5
- Promoter C57/BL6 mouse beta-globin minimal promoter
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 2
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SpeI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site SacII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GGACTAGTCCAATCTGCTCAGAGAGGACA
- 3′ sequencing primer GGCCGCGGGATGTCTGTTTCTGAGGTTGC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
All PCR was performed using the High Fidelity Advantage 2 PCR Kit (Clontech). The Runx1 +23 enhancer (1) was PCR amplified from C57/BL6 mouse genomic DNA using the following primers: Forward (XhoI and BamHI sites added) 5’-GGCTCGAGGGATCCGGGGTGGGAGGTGTAAGTTC-3’ and Reverse (BglII and NotI sites added) 5’- GGGCGGCCGCAGATCTCAGGTGTCAGCAACCCATC -3’. The PCR fragment was gel purified, XhoI/BglII digested, ligated into XhoI/BamHI digested Tol2kit (2) #228 p5E-MCS vector and sequence verified. The mouse beta-globin minimal promoter was PCR amplified from C57/BL6 mouse genomic DNA using the following primers: Forward (SpeI site added) 5’-GGACTAGTCCAATCTGCTCAGAGAGGACA-3’ and Reverse (SacII site added) 5’-GGCCGCGGGATGTCTGTTTCTGAGGTTGC-3’. The beta-globin minimal promoter and Runx1+23 5’ entry vector were SpeI/SacII digested and ligated together. Multisite Gateway reactions were performed according to the Invitrogen protocol.
1. Nottingham, W. T., Jarratt, A., Burgess, M., Speck, C. L., Cheng, J.-F., Prabhakar, S., et al. (2007). Runx1-mediated hematopoietic stem-cell emergence is controlled by a Gata/Ets/SCL-regulated enhancer. Blood, 110(13), 4188–4197. http://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-07-100883
2. Kwan, K. M., Fujimoto, E., Grabher, C., Mangum, B. D., Hardy, M. E., Campbell, D. S., et al. (2007). The Tol2kit: a multisite gateway-based construction kit for Tol2 transposon transgenesis constructs. Developmental Dynamics : an Official Publication of the American Association of Anatomists, 236(11), 3088–3099. http://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21343
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
p5E-Runx1+23 was a gift from Owen Tamplin & Leonard Zon (Addgene plasmid # 69602 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:69602 ; RRID:Addgene_69602) -
For your References section:
Hematopoietic stem cell arrival triggers dynamic remodeling of the perivascular niche. Tamplin OJ, Durand EM, Carr LA, Childs SJ, Hagedorn EJ, Li P, Yzaguirre AD, Speck NA, Zon LI. Cell. 2015 Jan 15;160(1-2):241-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.032. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.032 PubMed 25594182