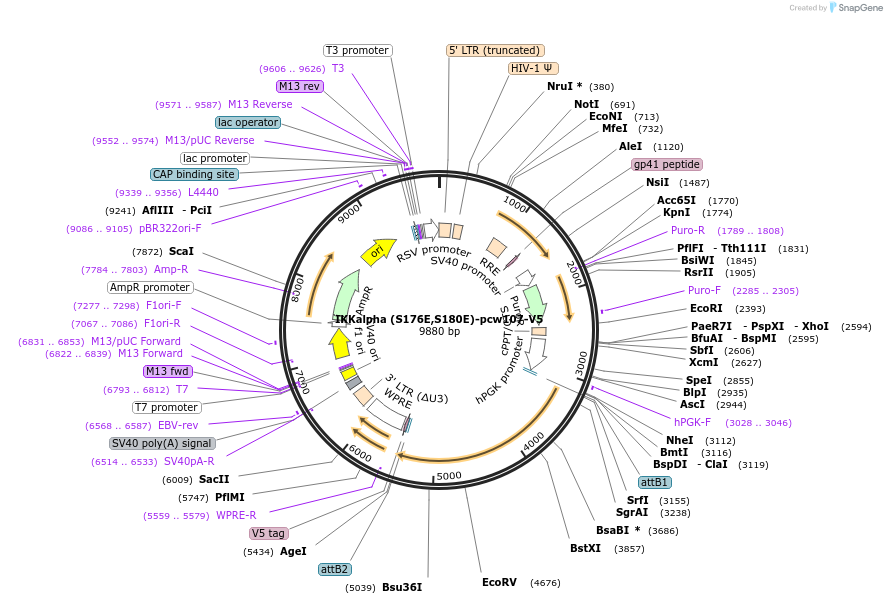
-
Purposewhen used to produce lentivirus, express physiological levels of insert
-
Depositing Labs
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 64608 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcw107 (V5)
-
Backbone manufacturerJohn Doench/Kathleen Ottina
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 9240
-
Vector typeLentiviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCHUK
-
Alt nameNM_001278.3
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)2238
-
MutationS176E, S180E
-
Entrez GeneCHUK (a.k.a. BPS2, IKBKA, IKK-1, IKK-alpha, IKK1, IKKA, NFKBIKA, TCF16)
- Promoter PGK
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- V5 (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gateway Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer hPGK-F
- 3′ sequencing primer WPRE-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byMichael Karin Lab, UCSD
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
CCGG (N-term barcode, 17 nt upstream of CDS start). Working name: CTK-C1-V5
Addgene NGS results found a V246A variant in the IKK-alpha open reading frame. This variant was present in the published plasmid and will function as described.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
IKKalpha (S176E,S180E)-pcw107-V5 was a gift from David Sabatini & Kris Wood (Addgene plasmid # 64608 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:64608 ; RRID:Addgene_64608) -
For your References section:
Systematic identification of signaling pathways with potential to confer anticancer drug resistance. Martz CA, Ottina KA, Singleton KR, Jasper JS, Wardell SE, Peraza-Penton A, Anderson GR, Winter PS, Wang T, Alley HM, Kwong LN, Cooper ZA, Tetzlaff M, Chen PL, Rathmell JC, Flaherty KT, Wargo JA, McDonnell DP, Sabatini DM, Wood KC. Sci Signal. 2014 Dec 23;7(357):ra121. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa1877. 10.1126/scisignal.aaa1877 PubMed 25538079