-
PurposeInducible expression of GFP-Mps1 fusion in mammalian cells
-
Depositing Lab
-
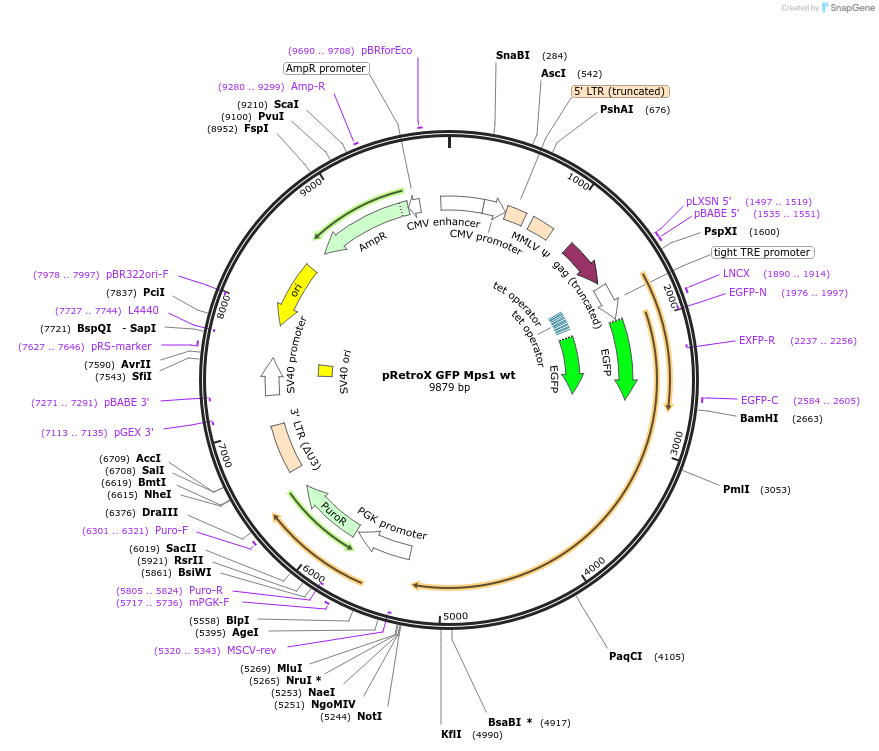
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 63702 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepRetrox
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 7305
- Total vector size (bp) 9555
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Retroviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameMps1
-
Alt nameTTK
-
Alt nameESK
-
Alt namePYT
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)2574
-
GenBank IDGene ID: 7272
-
Entrez GeneTTK (a.k.a. CT96, ESK, MPH1, MPS1, MPS1L1, PYT)
- Promoter tight TRE promoter
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer EGFP-C
- 3′ sequencing primer MSCV-rev
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pRetroX GFP Mps1 wt was a gift from Floris Foijer (Addgene plasmid # 63702 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:63702 ; RRID:Addgene_63702) -
For your References section:
Chromosome instability induced by Mps1 and p53 mutation generates aggressive lymphomas exhibiting aneuploidy-induced stress. Foijer F, Xie SZ, Simon JE, Bakker PL, Conte N, Davis SH, Kregel E, Jonkers J, Bradley A, Sorger PK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 16;111(37):13427-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400892111. Epub 2014 Sep 2. 10.1073/pnas.1400892111 PubMed 25197064