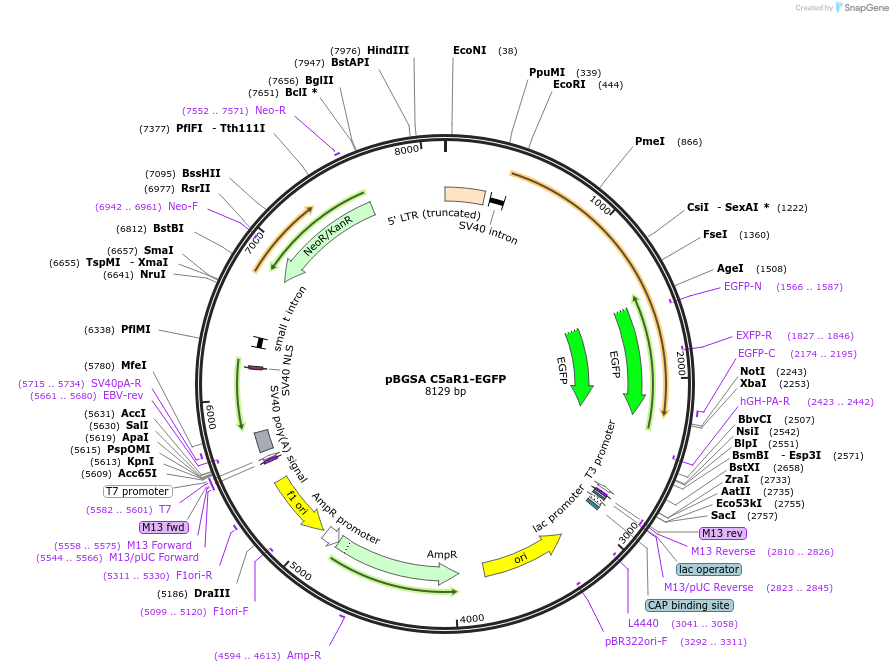
pBGSA C5aR1-EGFP
(Plasmid
#62612)
-
PurposeConstitutive expression of C5aR1-EGFP in mammalian cells
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 62612 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBGSA
-
Backbone manufacturerBruce Granger, PMID 8867788
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 7200
- Total vector size (bp) 9140
-
Modifications to backboneModified from pBS SK+
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameC5aR1
-
Alt nameC5aR
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1940
-
GenBank IDM62505
-
Entrez GeneC5AR1 (a.k.a. C5A, C5AR, C5R1, CD88)
- Promoter SRalpha
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XbaI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer cttctaggcctgtacgg
- 3′ sequencing primer EGFP-N
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pBGSA C5aR1-EGFP was a gift from Heini Miettinen (Addgene plasmid # 62612 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:62612 ; RRID:Addgene_62612) -
For your References section:
Different endocytosis pathways of the C5a receptor and the N-formyl peptide receptor. Suvorova ES, Gripentrog JM, Miettinen HM. Traffic. 2005 Feb;6(2):100-15. 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00256.x PubMed 15634211