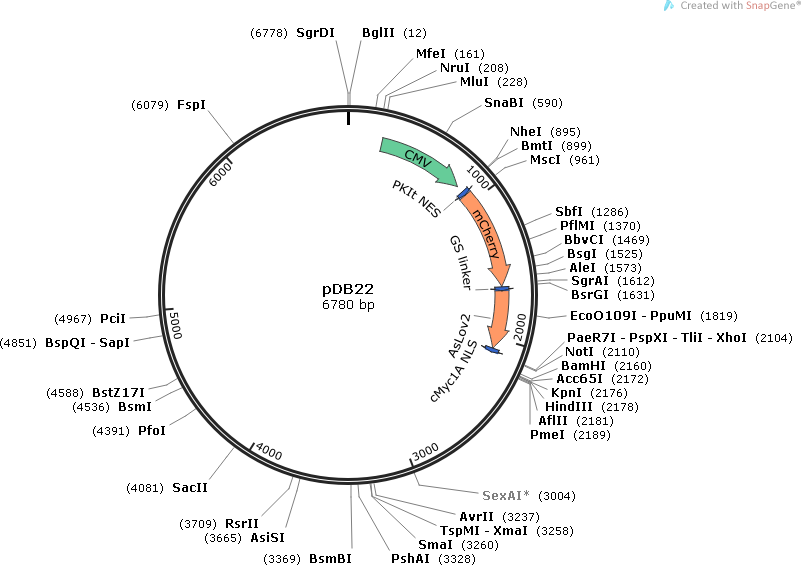
pDB22
(Plasmid
#61342)
-
PurposeMammalian expression of mCherry fused to LINuS, a light-inducible nuclear localization signal (cMycP1A NLS/PKIt NES)
-
Depositing Labs
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 61342 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA3.1(-)
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Total vector size (bp) 6780
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namemCherry
-
SpeciesSynthetic
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- PKIt NES (N terminal on insert)
- GS linker-AsLov2-cMyc1A NLS (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XhoI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-F
- 3′ sequencing primer BGHrev (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note that the mammalian selection marker in the vector backbone for this plasmid has not been verified by sequencing.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pDB22 was a gift from Barbara Di Ventura & Roland Eils (Addgene plasmid # 61342 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:61342 ; RRID:Addgene_61342) -
For your References section:
Engineering light-inducible nuclear localization signals for precise spatiotemporal control of protein dynamics in living cells. Niopek D, Benzinger D, Roensch J, Draebing T, Wehler P, Eils R, Di Ventura B. Nat Commun. 2014 Jul 14;5:4404. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5404. 10.1038/ncomms5404 PubMed 25019686