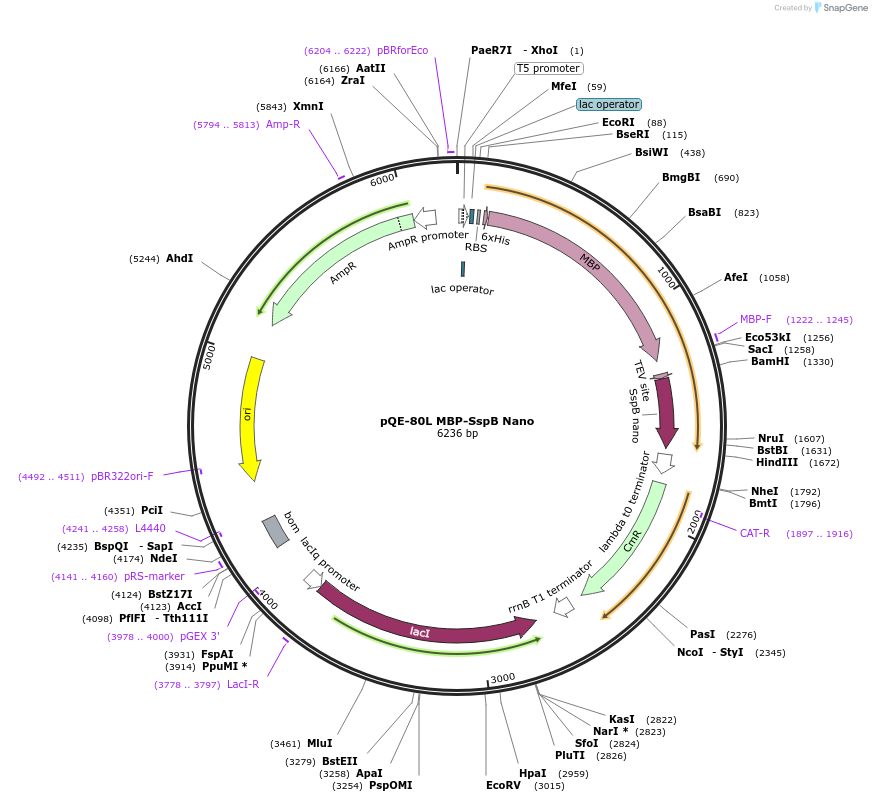
-
PurposeE. coli expression of SspB Nano
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 60409 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepQE-80L
-
Backbone manufacturerQiagen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5979
- Total vector size (bp) 6315
-
Modifications to backboneAdded N-terminal MBP
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameSspB nano
-
SpeciesE. Coli
-
Insert Size (bp)336
-
MutationY11K and A15E
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- His-MBP-TEV (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamH1 (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer pQE-80L Fwd
- 3′ sequencing primer pQE-80L Rev
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The SspB used in this construct contains two amino acid mutations that disrupt the natural dimerization of SspB. These mutations are Y11K and A15E (residue numbering from pdb code 1ou9). Here is the sequence around the mutated residues with the sites of mutation in parentheses: SSPKRP(K)LLR(E)YYDWLVDNS
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pQE-80L MBP-SspB Nano was a gift from Brian Kuhlman (Addgene plasmid # 60409 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:60409 ; RRID:Addgene_60409) -
For your References section:
Engineering an improved light-induced dimer (iLID) for controlling the localization and activity of signaling proteins. Guntas G, Hallett RA, Zimmerman SP, Williams T, Yumerefendi H, Bear JE, Kuhlman B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 6;112(1):112-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417910112. Epub 2014 Dec 22. 10.1073/pnas.1417910112 PubMed 25535392