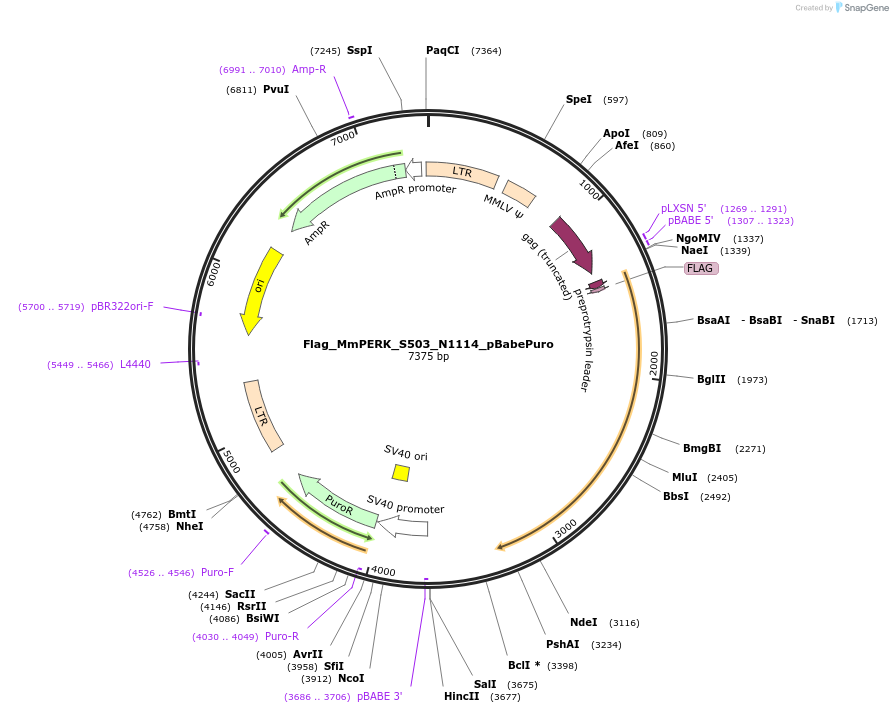
Flag_MmPERK_S503_N1114_pBabePuro
(Plasmid
#58423)
-
Purposeretroviral pBabe puro vector encoding N-terminally FLAG tagged mutant mouse PERK deleted from amino acids M1 to Y502. The remaining amino acids are S503 to N1114.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 58423 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBabe puro
-
Backbone manufacturerAddgene plasmid # 1764
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Retroviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Stbl2
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namePERK
-
Alt nameEukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3
-
Alt namePRKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
-
Alt nameEif2ak3
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
MutationDeleted amino acids M1 to Y502
-
Entrez GeneEif2ak3 (a.k.a. Pek, Perk)
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- preprotrypsin signal sequence (N terminal on insert)
- FLAG
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer pLXSN 5
- 3′ sequencing primer pBABE-3 (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
Flag_MmPERK_S503_N1114_pBabePuro was a gift from David Ron (Addgene plasmid # 58423 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:58423 ; RRID:Addgene_58423) -
For your References section:
Membrane lipid saturation activates endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response transducers through their transmembrane domains. Volmer R, van der Ploeg K, Ron D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 19;110(12):4628-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217611110. Epub 2013 Mar 4. 10.1073/pnas.1217611110 PubMed 23487760