-
PurposeGreen fluorescent indicator for calcium imaging in the endoplasmic reticulum
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 58215 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
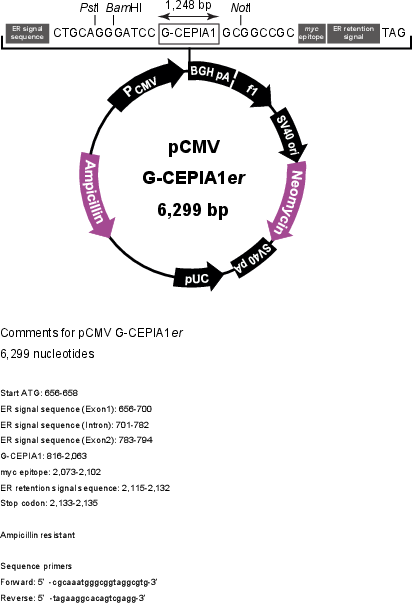
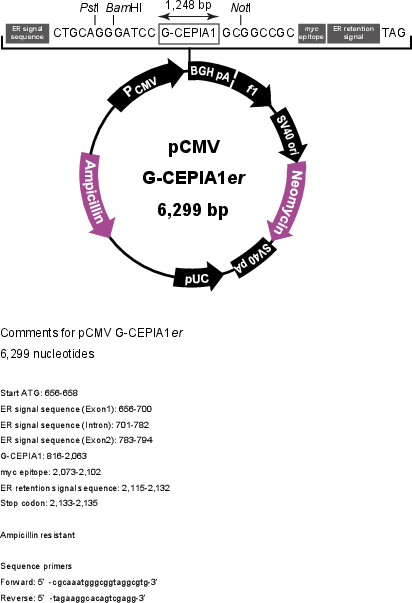
Vector backbonepCMV/myc/ER
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4819
- Total vector size (bp) 6299
-
Modifications to backboneNone.
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Stbl3
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameG-CEPIA1er
-
Alt namegreen fluorescent calcium-measuring organelle-entrapped protein indicator for the endoplasmic reticulum
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)1480
-
MutationG-GECO1.1 E299D M304L D328N N345K F360W G369S E372D V395E D401E
- Promoter CMV
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- myc (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site None (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XbaI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer cgcaaatgggcggtaggcgtg
- 3′ sequencing primer tagaaggcacagtcgagg (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV G-CEPIA1er was a gift from Masamitsu Iino (Addgene plasmid # 58215 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:58215 ; RRID:Addgene_58215) -
For your References section:
Imaging intraorganellar Ca(2+) at subcellular resolution using CEPIA. Suzuki J, Kanemaru K, Ishii K, Ohkura M, Okubo Y, Iino M. Nat Commun. 2014 Jun 13;5:4153. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5153. 10.1038/ncomms5153 PubMed 24923787