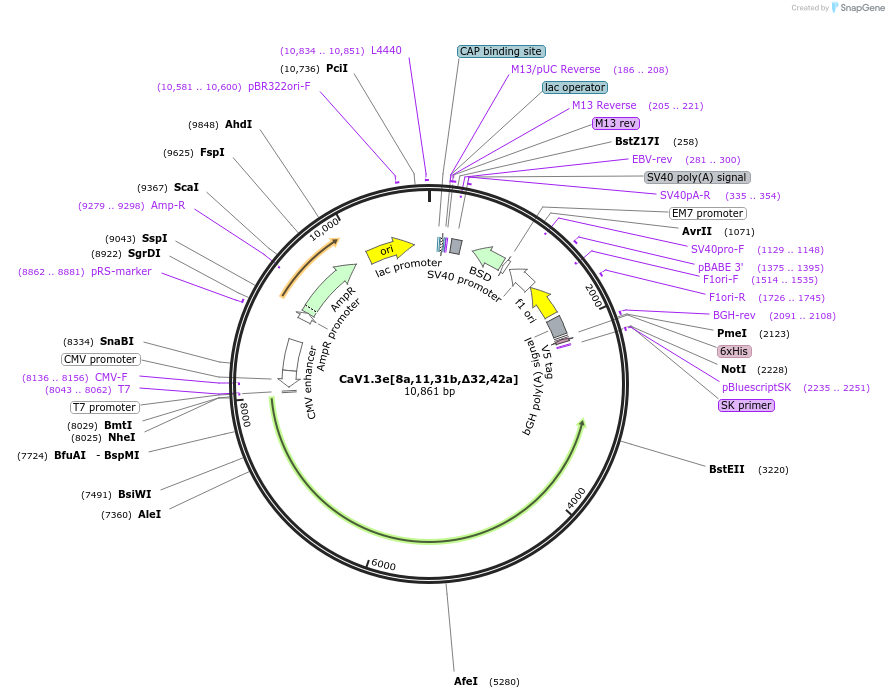
-
PurposeRepaired Addgene #26576 to agree with the rat ref sequence. Repairs are @: nt 3310 (GTG->GCG) [Val->Ala]; nt 731 (TCA->GGA) [Ser->Gly].
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 49333 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA6/V5-His ABC
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5100
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Top10F'
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCACNA1D
-
Alt namecalcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1D subunit
-
Alt nameCav1.3
-
SpeciesR. norvegicus (rat)
-
Insert Size (bp)5700
-
MutationContains exons 8a, 11, 31b and 42a.Deletion of exon 32.
-
Entrez GeneCacna1d
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-Fwd
- 3′ sequencing primer BGH-rev
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Isolated from superior cervical ganglia.
For more information about this plasmid: http://neuroscience.brown.edu/LipscombeLab/homepage/otherpages/clonespage/clonespage1.htm
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
CaV1.3e[8a,11,31b,Δ32,42a] was a gift from Diane Lipscombe (Addgene plasmid # 49333 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:49333 ; RRID:Addgene_49333) -
For your References section:
Neuronal Ca(V)1.3alpha(1) L-type channels activate at relatively hyperpolarized membrane potentials and are incompletely inhibited by dihydropyridines. Xu W, Lipscombe D. J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 15. 21(16):5944-51. PubMed 11487617