-
Purposeadeno-associated virus (AAV) encoding a green fluorescent protein
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 49055 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Want a viral vector made from this plasmid?
Make a packaging request and we'll get back to you.
Please log in to submit a packaging request.
-
SerotypeSelect serotype for details See details about
-
PricingSelect serotype and quantity $ USD for preparation of µL virus + $32 USD for plasmid.
-
How this works
- Place a request for a quantity of 2 (0.2 mL), 10 (1 mL), 25 (2.5 mL), or 50 (5 mL). Our all-inclusive pricing includes DNA production and QC.
- Addgene will quickly confirm that we can produce a high-quality prep for you.
- Track your request and place an order from within your account. Payment information must be added before we can begin processing your order.
- Receive your prep in 6–9 weeks after the MTA is approved by your organization.
- Learn more about our Packaged on Request Service.
Backbone
-
Vector backboneadeno-associated viral (AAVsp)
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6204
- Total vector size (bp) 7074
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Top10
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameeGFP
-
Alt nameEnhanced Green Fluorescent Protein
-
SpeciesAequorea victoria green
-
Insert Size (bp)720
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SfiI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site PmeI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer tagccacaccagccaccact
- 3′ sequencing primer caacgtgctggtctgtgtg
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
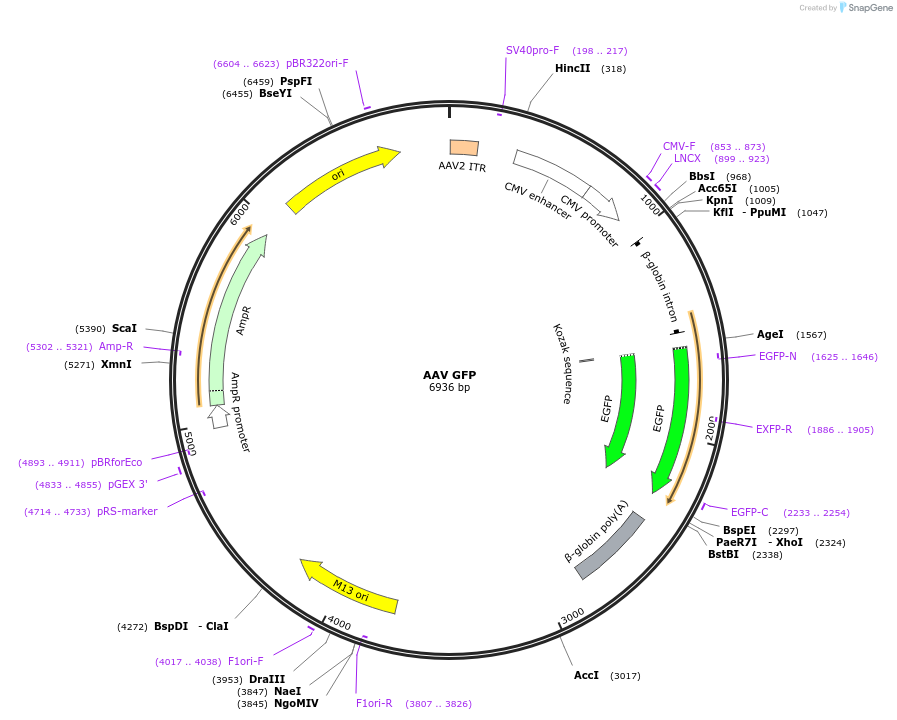
Expression of GFP is driven by a CMV promoter with a splice donor/acceptor sequence (SD/SA) and flanked by inverted terminal repeats (ITRs).
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
AAV GFP was a gift from Fred Gage (Addgene plasmid # 49055 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:49055 ; RRID:Addgene_49055) -
For your References section:
Adeno-associated virus effectively mediates conditional gene modification in the brain. Kaspar BK, Vissel B, Bengoechea T, Crone S, Randolph-Moore L, Muller R, Brandon EP, Schaffer D, Verma IM, Lee KF, Heinemann SF, Gage FH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Feb 19;99(4):2320-5. Epub 2002 Feb 12. 10.1073/pnas.042678699 PubMed 11842206