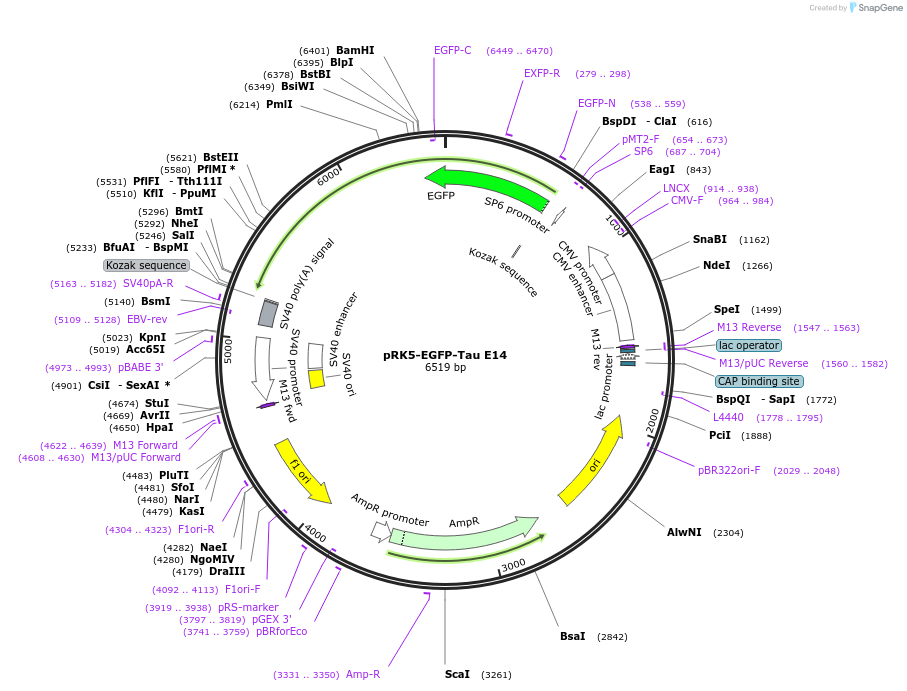
-
Purposeexpresses EGFP tagged Tau E14 in mammalian cells
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 46907 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepRK5
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameTau E14
-
Alt nameTau
-
Alt namemicrotubule-associated protein tau
-
Alt nameMAPT
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Mutationall 14 S/P or T/P amino acid residues (T111, T153, T175, T181, S199, S202, T205, T212, T217, T231, S235, S396, S404, and S422; numbering based on the longest 441-amino acid brain isoform of htau) to glutamate
-
Entrez GeneMAPT (a.k.a. DDPAC, FTD1, FTDP-17, MAPTL, MSTD, MTBT1, MTBT2, PPND, PPP1R103, TAU, Tau-PHF6, tau-40)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site Cla1 (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site SalI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer SP6
- 3′ sequencing primer SV40pA-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
WT htau construct (Addgene plasmid 46904) was used as a template to make mutations and contains human four-repeat tau lacking the N-terminal sequences (4R0N) and contains exons 1, 4 and 5, 7, and 9–13, intron 13, and exon 14.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pRK5-EGFP-Tau E14 was a gift from Karen Ashe (Addgene plasmid # 46907 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:46907 ; RRID:Addgene_46907) -
For your References section:
Tau mislocalization to dendritic spines mediates synaptic dysfunction independently of neurodegeneration. Hoover BR, Reed MN, Su J, Penrod RD, Kotilinek LA, Grant MK, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Lanier LM, Yuan LL, Ashe KH, Liao D. Neuron. 2010 Dec 22;68(6):1067-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.030. 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.030 PubMed 21172610