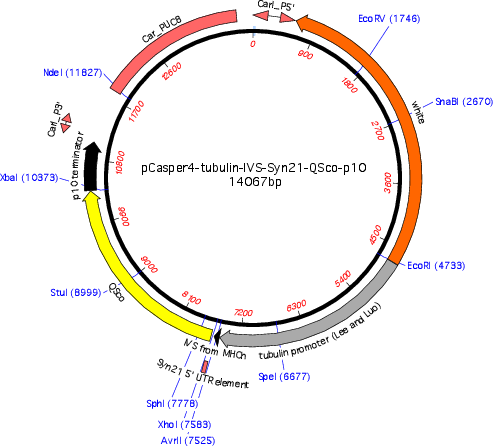
pCasper4-tubulin-IVS-Syn21-QSco-p10
(Plasmid
#46132)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 46132 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCasper4-tubulinP
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 11431
- Total vector size (bp) 14067
-
Modifications to backboneIntroduced IVS and Syn21 into 5' UTR. Removed SV40 terminator, and replaced with p10 terminator.
-
Vector typeInsect Expression
-
Selectable markerswhite
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameQSco
-
Alt nameQS codon optimized
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)2757
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer tubP-F:TTTCTATGCTGCTGGAACGC (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note that Addgene's sequencing results found a single nucleotide mismatch at bp# 5036 in the tubulin promoter when compared to the full plasmid sequence. The depositing laboratory states that this difference is not a concern for the function of the plasmid.
Please see this additional reference https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20434990 for more information on the Q-system.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCasper4-tubulin-IVS-Syn21-QSco-p10 was a gift from Christopher Potter (Addgene plasmid # 46132 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:46132 ; RRID:Addgene_46132) -
For your References section:
Improved and expanded Q-system reagents for genetic manipulations. Riabinina O, Luginbuhl D, Marr E, Liu S, Wu MN, Luo L, Potter CJ. Nat Methods. 2015 Jan 12. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3250. 10.1038/nmeth.3250 PubMed 25581800