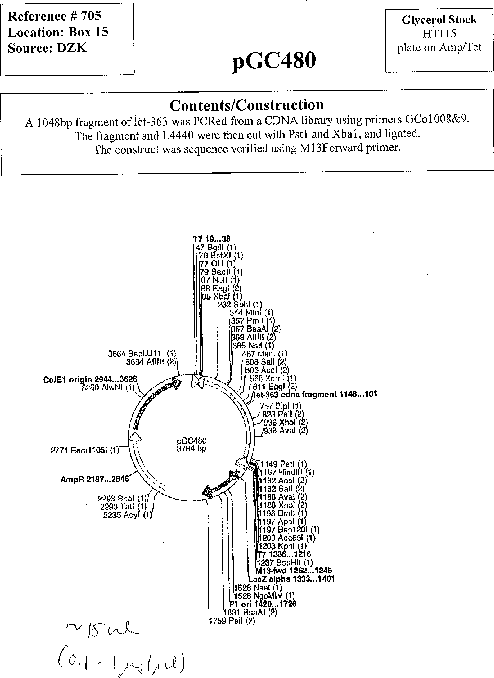
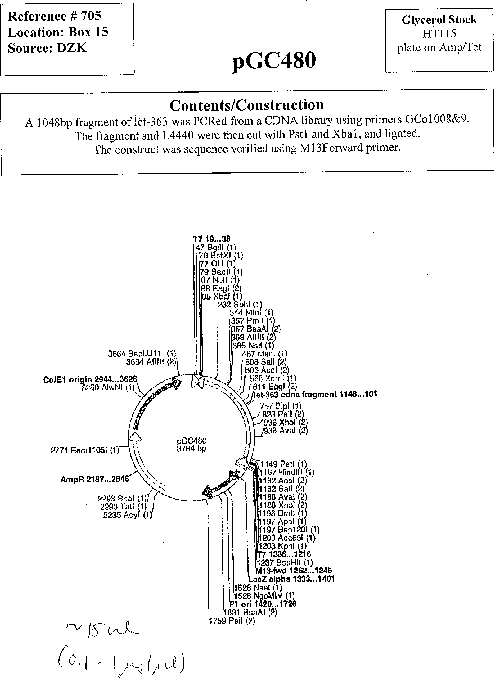
pGC480
(Plasmid
#42600)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Full plasmid sequence is not available for this item.
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 42600 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneL4440
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 2790
- Total vector size (bp) 3838
-
Vector typeRNAi
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin and Tetracycline, 100 & 10 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Growth instructionsGrow on LB + Amp + Tet plates. For RNAi feeding of worms grow LB liquid cultures 16 hours with only Amp.
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namelet-363 cDNA
-
gRNA/shRNA sequencelet-363
-
SpeciesC. elegans (nematode)
- Promoter T7
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site PstI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XbaI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer M13F
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
This plasmid can be kept in DH5alpha cells but does not work for RNAi in that strain. For RNAi, please transform DNA into the HT115 strain.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pGC480 was a gift from Jane Hubbard (Addgene plasmid # 42600 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:42600 ; RRID:Addgene_42600) -
For your References section:
S6K links cell fate, cell cycle and nutrient response in C. elegans germline stem/progenitor cells. Korta DZ, Tuck S, Hubbard EJ. Development. 2012 Mar;139(5):859-70. doi: 10.1242/dev.074047. Epub 2012 Jan 25. 10.1242/dev.074047 PubMed 22278922
Map uploaded by the depositor.