-
PurposeNon-integrating (episomal) expression of EGFP
-
Depositing Lab
-
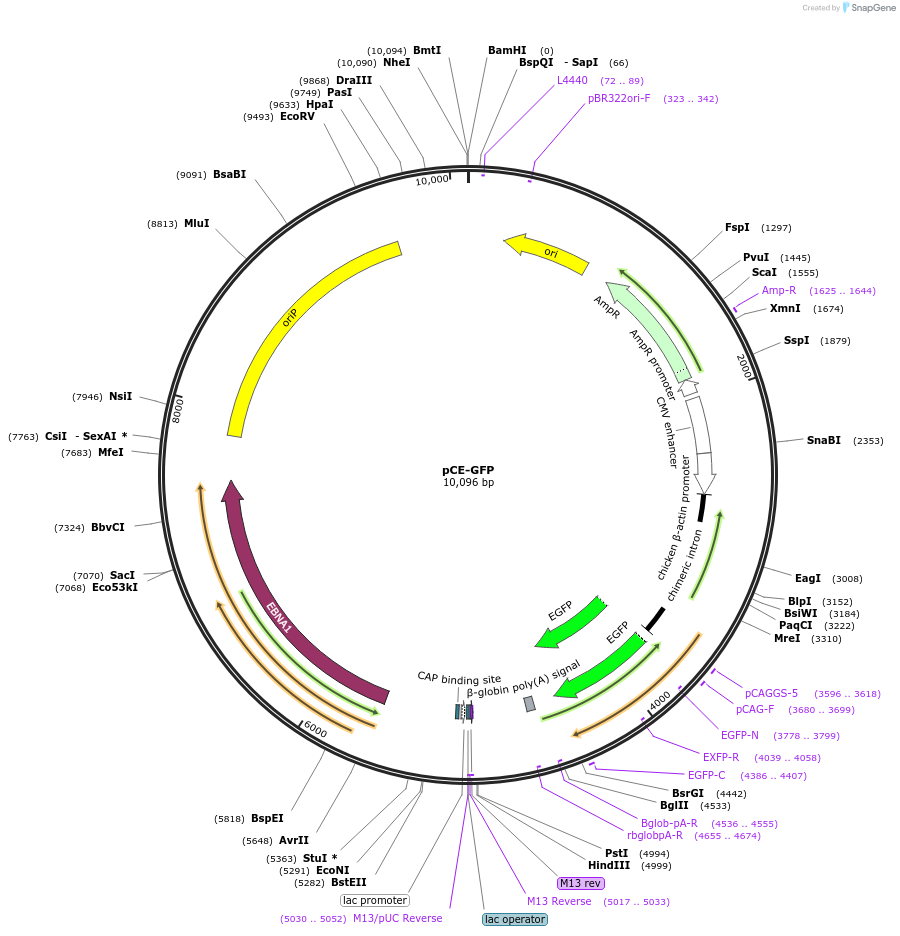
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 41858 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCE
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 9364
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameeGFP
-
Insert Size (bp)732
- Promoter CAG
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer pCAG-F
- 3′ sequencing primer TTAGCCAGAAGTCAGATGCTC (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made bypCEP4 is from Invitrogen. CAG Promoter was from Dr. Jun-ichi Miyazaki of Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine. In publication using this plasmid, please cite: Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 108:193-200, 1991. Niwa, H., Yamamura, K. & Miyazaki, J.
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCE-GFP was a gift from Shinya Yamanaka (Addgene plasmid # 41858 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:41858 ; RRID:Addgene_41858) -
For your References section:
An Efficient Non-viral Method to Generate Integration-Free Human iPS Cells from Cord Blood and Peripheral Blood Cells. Okita K, Yamakawa T, Matsumura Y, Sato Y, Amano N, Watanabe A, Goshima N, Yamanaka S. Stem Cells. 2012 Nov 29. doi: 10.1002/stem.1293. 10.1002/stem.1293 PubMed 23193063