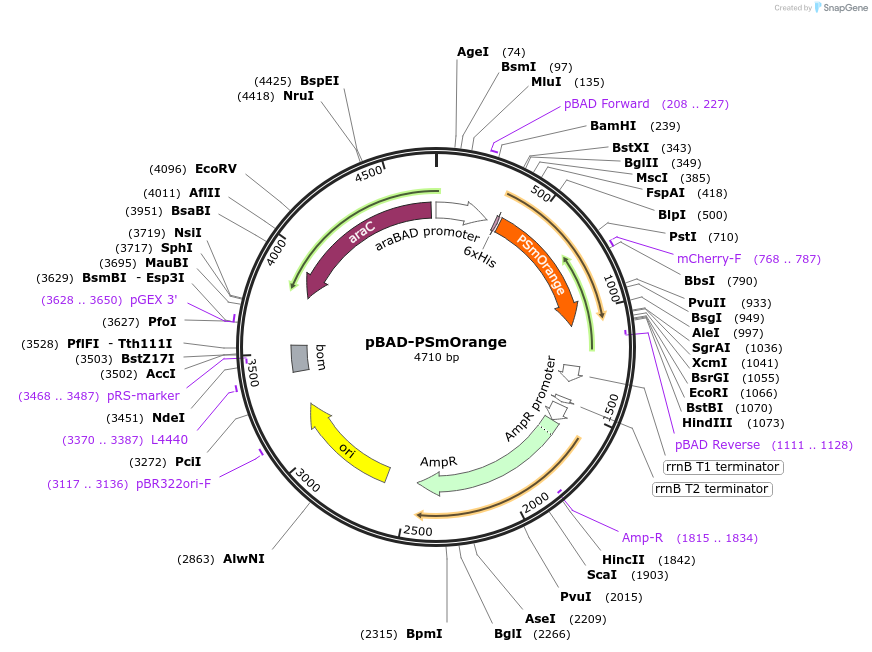
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 31886 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBAD
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4100
-
Modifications to backboneATGGGGAGCCACCATCACCATCACCATGGCAGATCT instead of ATGGGGGGTTCTCATCATCATCATCATCATGGTATGGCTAGCATGACTGGTGGACAGCAAATGGGTCGGGATCTGTACGACGATGACGATAAGGATCCGAGCTCG
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Top10/P3
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namePSmOrange
-
Insert Size (bp)711
-
MutationS21T, Q63L, F100Y, L125M, K166R, P192S (mutations are relative to mOrange but numbering is relative to EGFP)
-
GenBank IDJN_376081
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BglII (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer pBAD-fwd
- 3′ sequencing primer pBAD-rev (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pBAD-PSmOrange was a gift from Vladislav Verkhusha (Addgene plasmid # 31886 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:31886 ; RRID:Addgene_31886) -
For your References section:
A photoswitchable orange-to-far-red fluorescent protein, PSmOrange. Subach OM, Patterson GH, Ting LM, Wang Y, Condeelis JS, Verkhusha VV. Nat Methods. 2011 Jul 31;8(9):771-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1664. 10.1038/nmeth.1664 PubMed 21804536