-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 28176 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
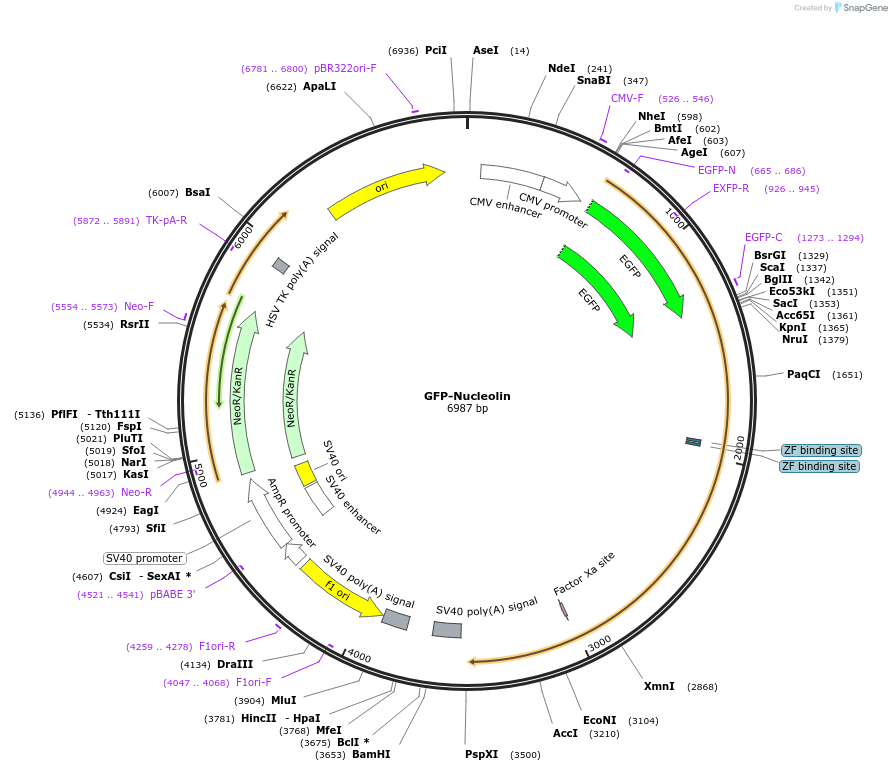
Vector backbonepEGFPC1
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4700
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameNucleolin
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)2100
-
Entrez GeneNCL (a.k.a. C23, Nsr1)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- GFP (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site KpnI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer EGFP-C
- 3′ sequencing primer SV40-pA-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Addgene Notes
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byFrance Carrier
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
There are a few mutations (K132R, K141E, & K142E and G680S) in the nucleolin but they are not thought to affect function.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
GFP-Nucleolin was a gift from Michael Kastan (Addgene plasmid # 28176 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:28176 ; RRID:Addgene_28176) -
For your References section:
Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin. Takagi M, Absalon MJ, McLure KG, Kastan MB. Cell. 2005 Oct 7. 123(1):49-63. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.034 PubMed 16213212