-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Full plasmid sequence is not available for this item.
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 27554 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMV4
-
Backbone manufacturerDr. David Russell, UTSW
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4874
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameNIK
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
MutationNIK starts at amino acid 3; C52R and R139H mutations when compared to NP_003945.2
-
Entrez GeneMAP3K14 (a.k.a. FTDCR1B, HS, HSNIK, IMD112, NIK)
- Promoter CMV
-
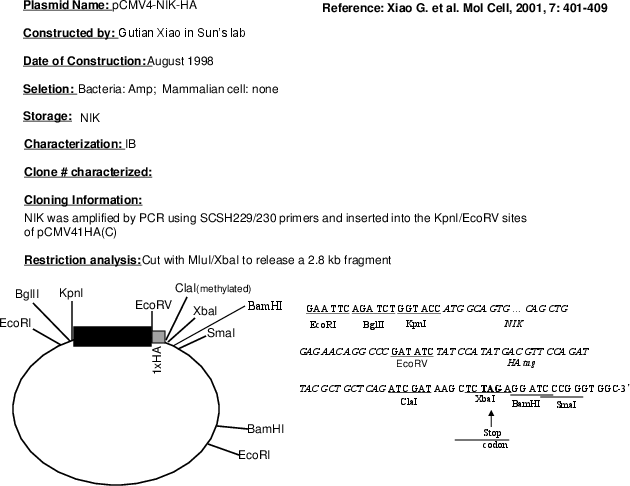
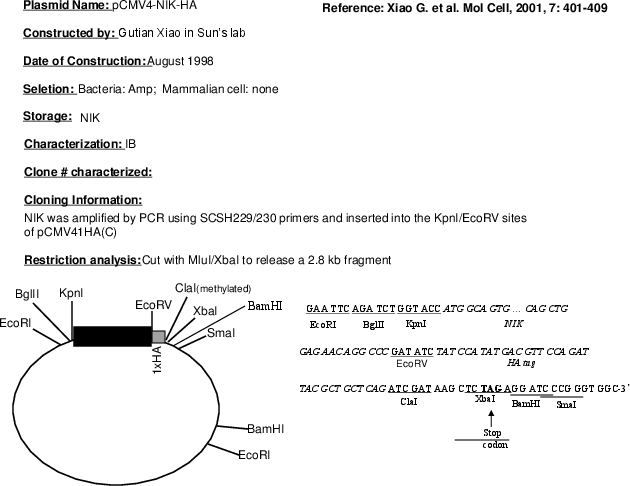
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- HA (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site KpnI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRV (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-F
- 3′ sequencing primer hGH-pA-R (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byTo create pCMV4-HA-NIK, we PCR amplified the NIK cDNA using the Flag-NIK plasmid (obtained from Dr. David Wallach with MTA) as template.
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
According to the depositing laboratory, the differences in NIK compared to GenBank reference sequence NP_003945.2 do not affect the function of NIK.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV4-NIK-HA was a gift from Shao-Cong Sun (Addgene plasmid # 27554 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:27554 ; RRID:Addgene_27554) -
For your References section:
Negative regulation of the nuclear factor kappa B-inducing kinase by a cis-acting domain. Xiao G, Sun SC. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 14. 275(28):21081-5. 10.1074/jbc.M002552200 PubMed 10887201
Map uploaded by the depositor.