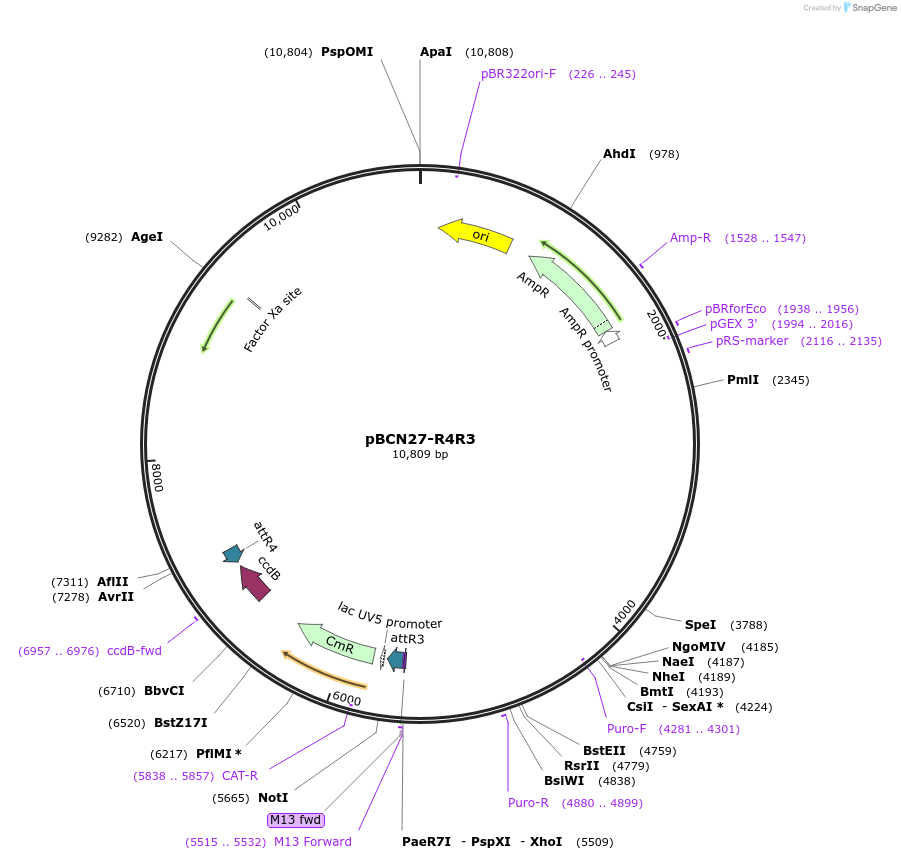
pBCN27-R4R3
(Plasmid
#26346)
-
Purpose(Empty Backbone)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 26346 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCJF150
- Backbone size (bp) 10809
-
Vector typeWorm Expression
-
Selectable markersPuromycin ; unc-119
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Chloramphenicol and Ampicillin, 25 & 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)ccdB Survival
-
Growth instructionsccdB Survival T1 phage resistant cells.
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameNone
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site AttR4 (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site AttR3 (destroyed during cloning)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byPuromycin resistance gene from pBabePuro (Addgene). rpl-28 promoter and let-858 3'UTR sequences from pPD129.57 vector (Addgene).
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The Prpl-28::PuroR::let-858_3'UTR cassette was inserted into the backbone of pCFJ150 to create a puromycin-selectable MosSCI vector for single copy integration in worms at the ttTi5605.
This is a Gateway 3-fragment compatible destination vector.
It contains AttR4 and AttR3 sites (not AttR1 and AttR2 sites as identified automatically by the Addgene algorithm).
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pBCN27-R4R3 was a gift from Ben Lehner (Addgene plasmid # 26346 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:26346 ; RRID:Addgene_26346) -
For your References section:
Rapid selection of transgenic C. elegans using antibiotic resistance. Semple JI, Garcia-Verdugo R, Lehner B. Nat Methods. 2010 Aug 22. ():. 10.1038/nmeth.1495 PubMed 20729840