-
PurposeMammalian expression of human E2F2 with HA tag
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 24226 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
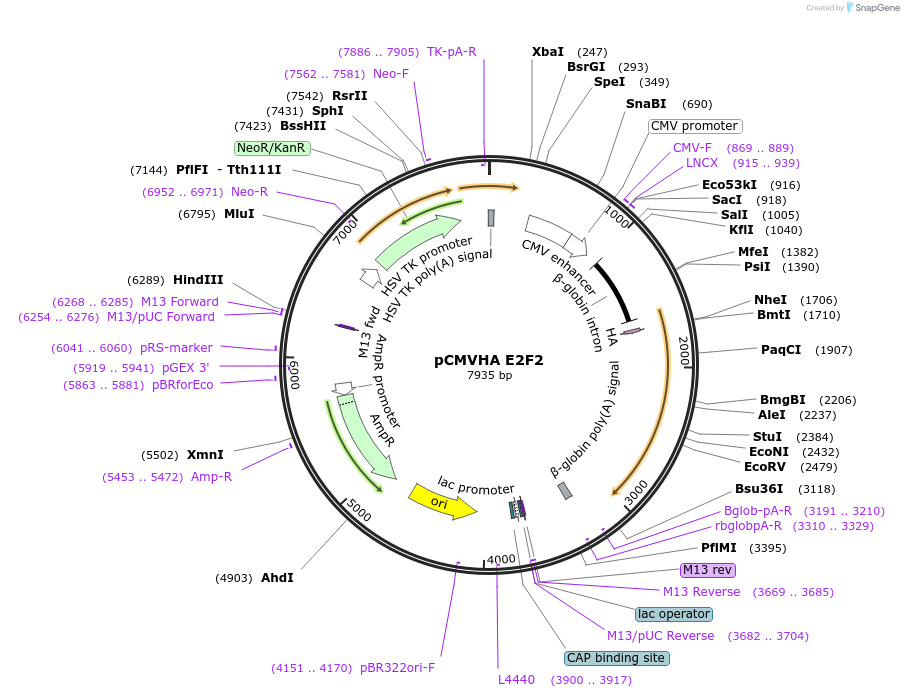
Vector backbonepCMVHANeoBam
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6600
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameE2F2
-
Alt nameE2F-2
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1300
-
Entrez GeneE2F2 (a.k.a. E2F-2)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- HA (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BamHI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer Bglob-intron-F
- 3′ sequencing primer Bglob-pA-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Insert check with SalI, which leads to three fragments 4.7kb 1,8kb 0,35kb. E2F1 cDNA can be removed by BamHI digest.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMVHA E2F2 was a gift from Kristian Helin (Addgene plasmid # 24226 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:24226 ; RRID:Addgene_24226) -
For your References section:
Deregulated expression of E2F family members induces S-phase entry and overcomes p16INK4A-mediated growth suppression. Lukas J, Petersen BO, Holm K, Bartek J, Helin K. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Mar . 16(3):1047-57. PubMed 8622649