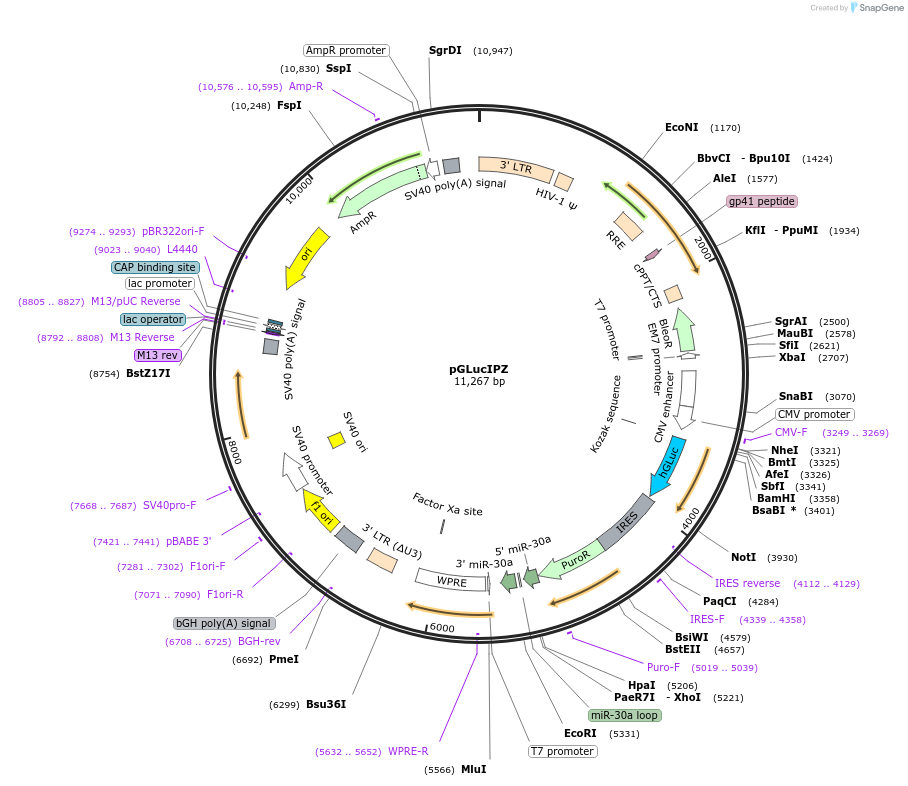
pGLucIPZ
(Plasmid
#228703)
-
PurposeConstitutive expression of Gaussia luciferase, puromycin N-acetyl-transferase and shRNAmir of interest
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 228703 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 * | |
* Log in to view industry pricing.
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepGIPZ
-
Backbone manufacturerOpen Biosystems
- Total vector size (bp) 11267
-
Modifications to backboneDeletion of an EcoRI site in the Hygromycin resistance gene
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Lentiviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert nameGaussia luciferase
-
Alt nameGLuc
-
SpeciesGaussia princeps
-
Insert Size (bp)558
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 1
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site XhoI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer ATCAAAGAGATAGCAAGGTATTCAGTT
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert namenon-silencing shRNA
-
Alt namensh
-
Insert Size (bp)110
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pGLucIPZ was a gift from Thorsten Stiewe (Addgene plasmid # 228703 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:228703 ; RRID:Addgene_228703) -
For your References section:
Monitoring the dynamics of clonal tumour evolution in vivo using secreted luciferases. Charles JP, Fuchs J, Hefter M, Vischedyk JB, Kleint M, Vogiatzi F, Schafer JA, Nist A, Timofeev O, Wanzel M, Stiewe T. Nat Commun. 2014 Jun 3;5:3981. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4981. 10.1038/ncomms4981 PubMed 24889111