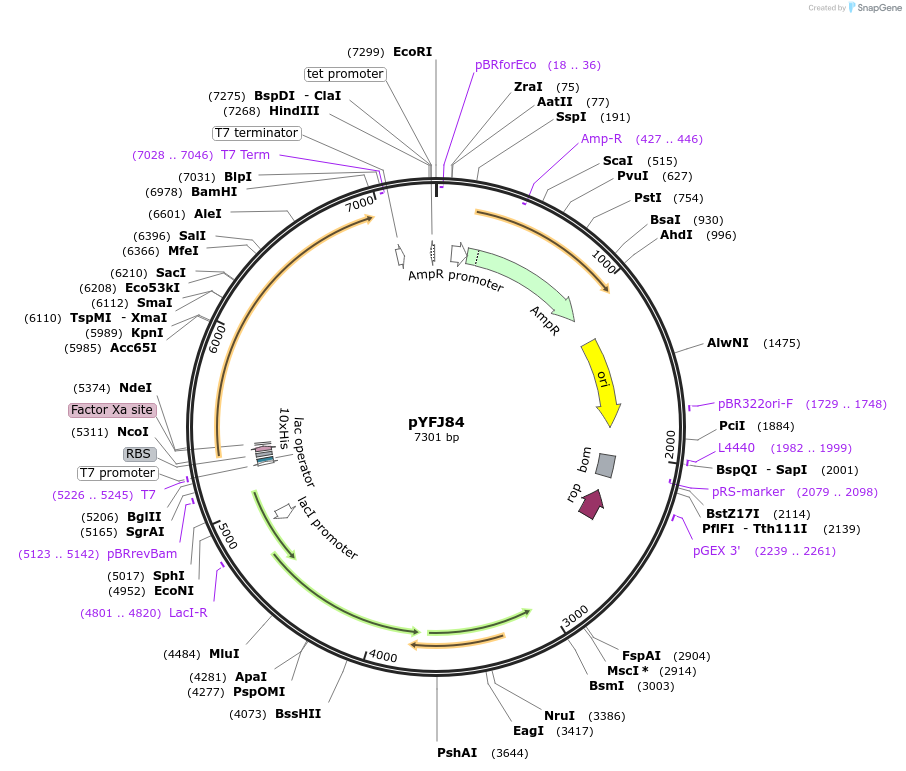
pYFJ84
(Plasmid
#227644)
-
PurposeVibrio harveyi acyl-ACP synthetase
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 227644 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepET16
-
Backbone manufacturerNovagen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5711
- Total vector size (bp) 7317
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Top10F'
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameAcyl-Acyl carrier protein synthetase
-
Alt nameAasS
-
SpeciesVibrio harveyi
-
Insert Size (bp)1664
- Promoter T7
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- 10xHis (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NdeI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BamHI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer Novagen T7 promoter primer TAATACGACTCACTA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byMy former student Dr Yanfang Jiang
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The enzyme is used to make substrates for fatty acid, polyketide and nonribosomal polypetide enzymes.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pYFJ84 was a gift from John Cronan (Addgene plasmid # 227644 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:227644 ; RRID:Addgene_227644) -
For your References section:
The soluble acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase of Vibrio harveyi B392 is a member of the medium chain acyl-CoA synthetase family. Jiang Y, Chan CH, Cronan JE. Biochemistry. 2006 Aug 22;45(33):10008-19. doi: 10.1021/bi060842w. 10.1021/bi060842w PubMed 16906759