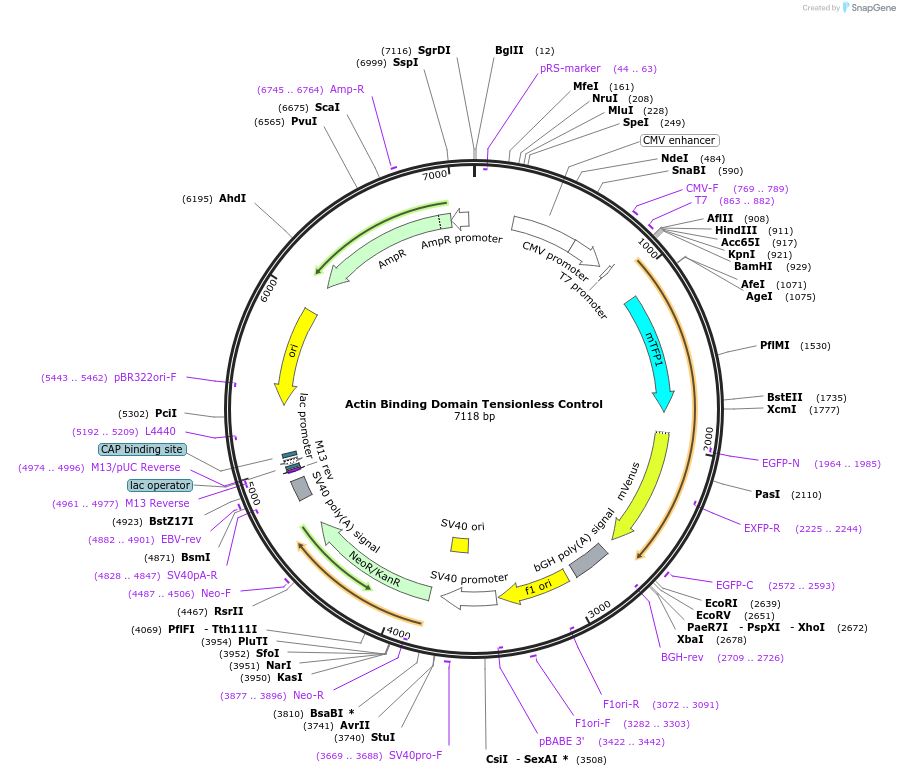
Actin Binding Domain Tensionless Control
(Plasmid
#215371)
-
PurposeExpresses Actin Binding Domain Tensionless Control (ABDTL), composed of Ftractin-Linker-TSMod. This is the unloaded control for Actin Binding Domain Tension Sensor (ABDTS).
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 215371 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA3.1
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5411
- Total vector size (bp) 7115
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameActin Binding Domain Tensionless Control
-
Alt nameADBTL
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)1704
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV Forward
- 3′ sequencing primer BGH Reverse
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byDyche Mullins (F-tractin and Linker 1 from Addgene plasmid # 58473) and Martin Schwartz (Original TSMod from Addgene plasmid # 26021).
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
F-tractin is based on the rat neuronal inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate 3-kinase A (ITPKA) actin-binding domain.
Please visit https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.01.10.575065v1 for bioRxiv preprint.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
Actin Binding Domain Tensionless Control was a gift from Brenton Hoffman (Addgene plasmid # 215371 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:215371 ; RRID:Addgene_215371) -
For your References section:
Detection of fluorescent protein mechanical switching in cellulo. Shoyer TC, Collins KL, Ham TR, Blanchard AT, Malavade JN, Johns BA, West JL, Hoffman BD. Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Jul 15;4(7):100815. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100815. Epub 2024 Jul 9. 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100815 PubMed 38986612