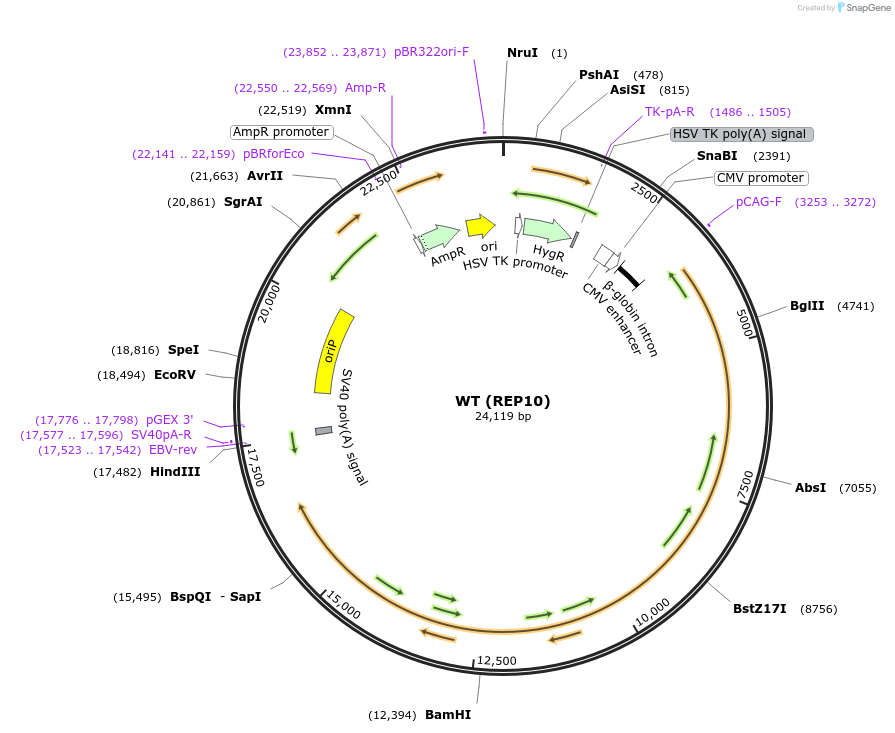
WT (REP10)
(Plasmid
#21368)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 21368 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepREP10
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 8500
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersHygromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Growth instructionsDH5a in dYT at 37oC
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameautosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type I
-
Alt namePKD1 wild-type
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)14000
-
GenBank IDL33243
-
Entrez GenePKD1 (a.k.a. PBP, PC1, Pc-1, TRPP1)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a
- 3′ sequencing primer n/a (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note that Addgene NGS observed a S999P mutation in the PKD1 ORF. The effect of this mutation in unknown.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
WT (REP10) was a gift from Gregory Germino (Addgene plasmid # 21368 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:21368 ; RRID:Addgene_21368) -
For your References section:
Cleavage of polycystin-1 requires the receptor for egg jelly domain and is disrupted by human autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease 1-associated mutations. Qian F, Boletta A, Bhunia AK, Xu H, Liu L, Ahrabi AK, Watnick TJ, Zhou F, Germino GG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 24. 99(26):16981-6. 10.1073/pnas.252484899 PubMed 12482949