-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 21266 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
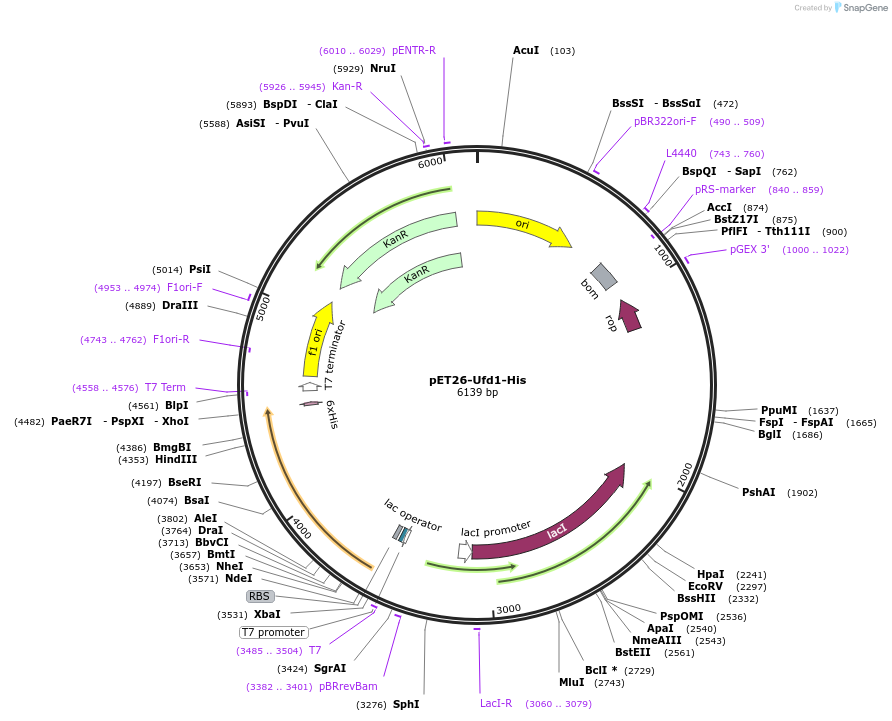
Vector backbonepET26
-
Backbone manufacturerNovagen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3000
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameUfd1
-
Alt nameUFD1L
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)921
-
Entrez GeneUfd1l (a.k.a. Ufd1)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- His (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NdeI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XhoI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Addgene Next-generation sequencing QC processes identified that the insert harbors truncations of the region encoding the first 4 amino acids and final amino acid of Ufd1, relative to the NCBI reference sequence NM_011672
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pET26-Ufd1-His was a gift from Hemmo Meyer (Addgene plasmid # 21266 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:21266 ; RRID:Addgene_21266) -
For your References section:
The AAA ATPase p97/VCP interacts with its alternative co-factors, Ufd1-Npl4 and p47, through a common bipartite binding mechanism. Bruderer RM, Brasseur C, Meyer HH. J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 26. 279(48):49609-16. 10.1074/jbc.M408695200 PubMed 15371428