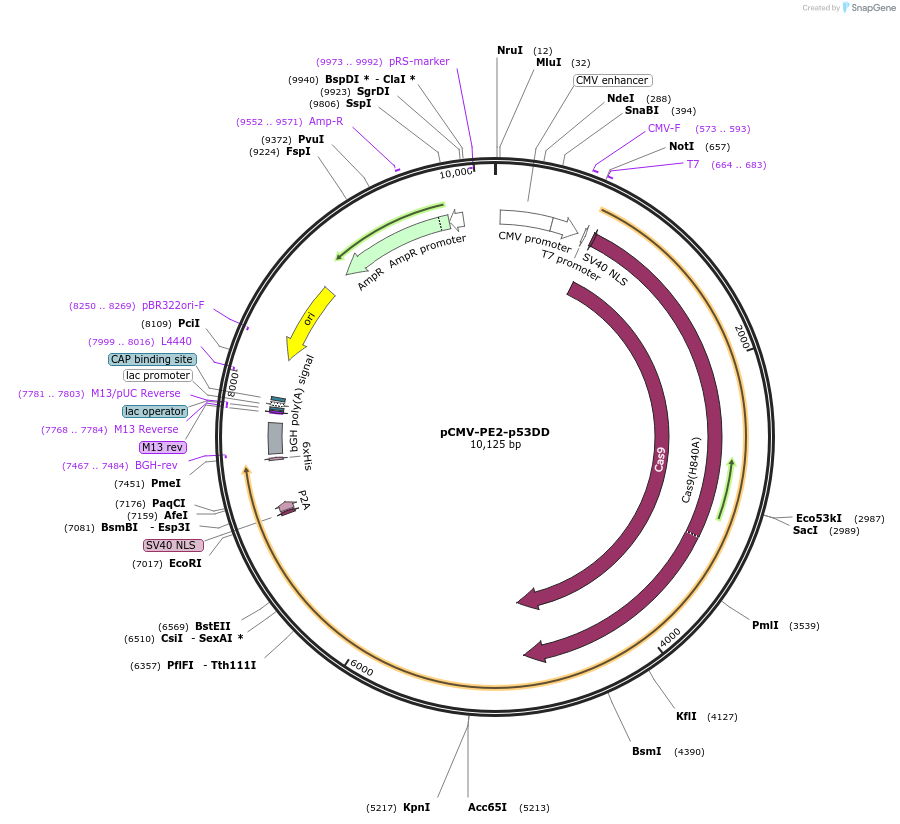
pCMV-PE2-p53DD
(Plasmid
#196582)
-
PurposeMammalian expression of SpCas9 prime editor 2 with P2A-p53DD
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 196582 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMV
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namePE2-P2A-mp53DD
-
Alt nameSV40_bpNLS-SpCas9(H840A)-SGGSx2-XTEN16-SGGSx2-MMLV_RT(D200N, T306K, W313F, T330P, L603W)-SV40_bpNLS
-
Alt nameTrp53 carboxy-terminal dominant-negative fragment
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse), Synthetic; SpCas9 is from Streptococcus pyogenes; MMLV_RT is from the Moloney murine leukemia virus
-
Insert Size (bp)6716
-
MutationΔ40-903
-
GenBank IDNM_011640
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer T7
- 3′ sequencing primer M13-rev (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byPE2 is from Addgene Plasmid #132775; p53DD is from Addgene Plasmid #41856.
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV-PE2-p53DD was a gift from Ting Zhou (Addgene plasmid # 196582 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:196582 ; RRID:Addgene_196582) -
For your References section:
Transient inhibition of p53 enhances prime editing and cytosine base-editing efficiencies in human pluripotent stem cells. Li M, Zhong A, Wu Y, Sidharta M, Beaury M, Zhao X, Studer L, Zhou T. Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 27;13(1):6354. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34045-7. 10.1038/s41467-022-34045-7 PubMed 36302757