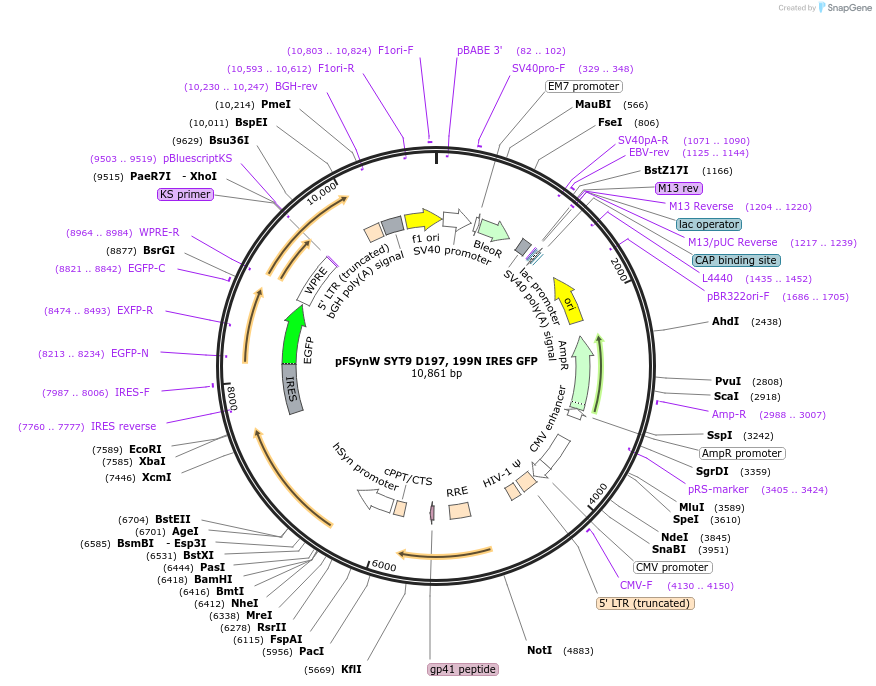
pFSynW SYT9 D197, 199N IRES GFP
(Plasmid
#195701)
-
PurposeLentiviral plasmid encoding SYT9 with D197, 199N mutations followed by an internal ribosomal entry site followed by EGFP under the human synapsin promoter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 195701 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneFUGW
-
Backbone manufacturerDavid Baltimore (Addgene plasmid # 14883)
-
Vector typeLentiviral
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameSyt9
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Mutationfull-length mouse SYT9 with D197, 199N mutations
-
Entrez GeneSyt5 (a.k.a. SytV)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site Unknown (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site Unknown (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
full-length mouse SYT9 with D197, 199N mutations; bicistronic EGFP expression
Please visit https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.04.18.488681v2 for bioRxiv preprint.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pFSynW SYT9 D197, 199N IRES GFP was a gift from Edwin Chapman (Addgene plasmid # 195701 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:195701 ; RRID:Addgene_195701) -
For your References section:
Synaptotagmin 9 Modulates Spontaneous Neurotransmitter Release in Striatal Neurons by Regulating Substance P Secretion. Seibert MJ, Evans CS, Stanley KS, Wu Z, Chapman ER. J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 1;43(9):1475-1491. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1857-22.2023. Epub 2023 Feb 2. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1857-22.2023 PubMed 36732068