-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
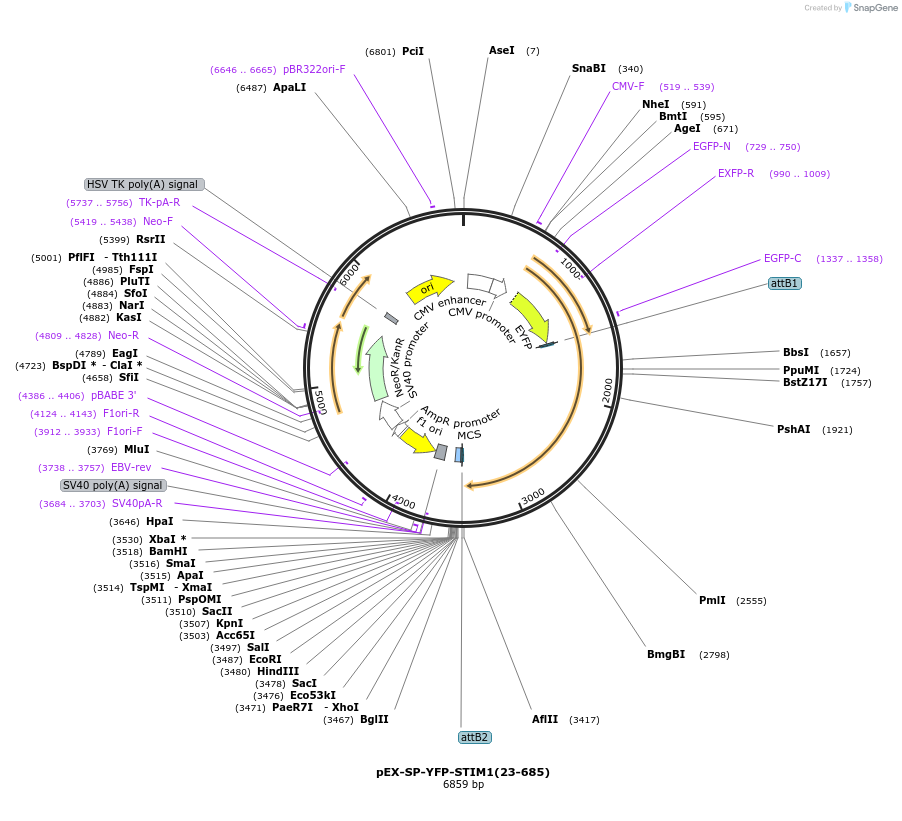
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 18857 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneGateway destination
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5000
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameStromal interaction molecule 1
-
Alt nameSTIM1
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1995
-
MutationYFP is inserted between residues 1-23 (signal peptide) and residues 23-685 of STIM1. V419A. Lab plasmid MK2002.
-
GenBank IDNM_003156
-
Entrez GeneSTIM1 (a.k.a. D11S4896E, GOK, IMD10, STRMK, TAM, TAM1)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- YFP (N terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gateway Cloning
- 5′ cloning site attB1 (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site attB2 (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a
- 3′ sequencing primer n/a
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pEX-SP-YFP-STIM1(23-685) was a gift from Tobias Meyer (Addgene plasmid # 18857 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:18857 ; RRID:Addgene_18857) -
For your References section:
STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Liou J, Kim ML, Heo WD, Jones JT, Myers JW, Ferrell JE, Meyer T. Curr Biol. 2005 Jul 12. 15(13):1235-41. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.055 PubMed 16005298