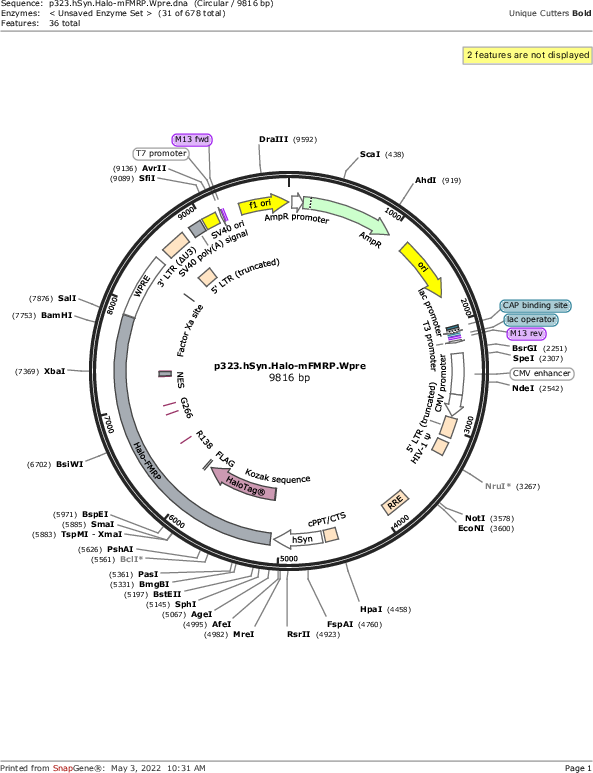
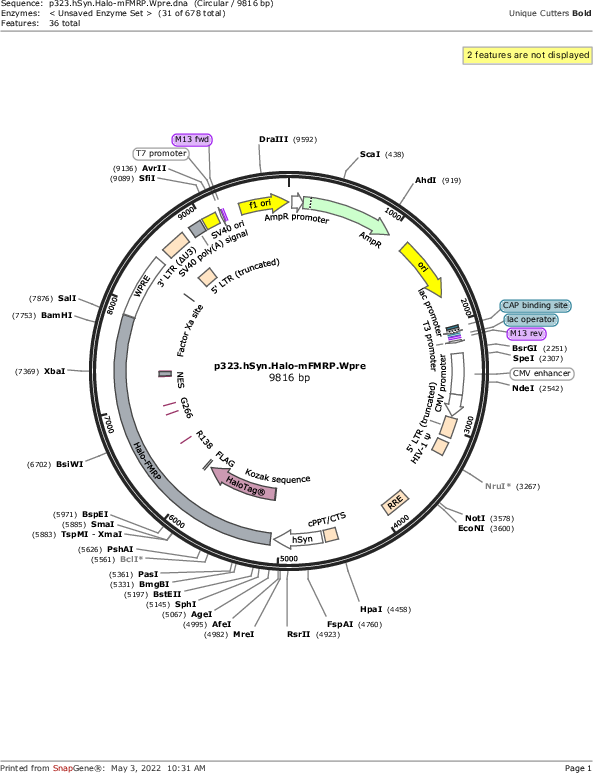
p323.hSyn.Halo-mFMRP.Wpre
(Plasmid
#185909)
-
PurposeExpresses FMRP fused to HaloTag for protein localization through fluorescence imaging
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 185909 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneLentiviral vector (Gen 3)
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 7000
- Total vector size (bp) 9800
-
Vector typeLentiviral
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameHaloTag fused to mouse Fragile X mental retardation protein
-
Alt nameHalo-FMRP
-
Alt nameHalo-mFMRP
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)2800
-
Entrez GeneCtsa (a.k.a. PPCA, Ppgb)
- Promoter hSyn (human Synapsin promoter)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- HaloTag (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site AgeI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site SalI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer hSyn promoter primer
- 3′ sequencing primer Wpre reverse primer (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
p323.hSyn.Halo-mFMRP.Wpre was a gift from Young J Yoon (Addgene plasmid # 185909 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:185909 ; RRID:Addgene_185909) -
For your References section:
Presynaptic FMRP and local protein synthesis support structural and functional plasticity of glutamatergic axon terminals. Monday HR, Kharod SC, Yoon YJ, Singer RH, Castillo PE. Neuron. 2022 Aug 17;110(16):2588-2606.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.05.024. Epub 2022 Jun 20. 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.05.024 PubMed 35728596