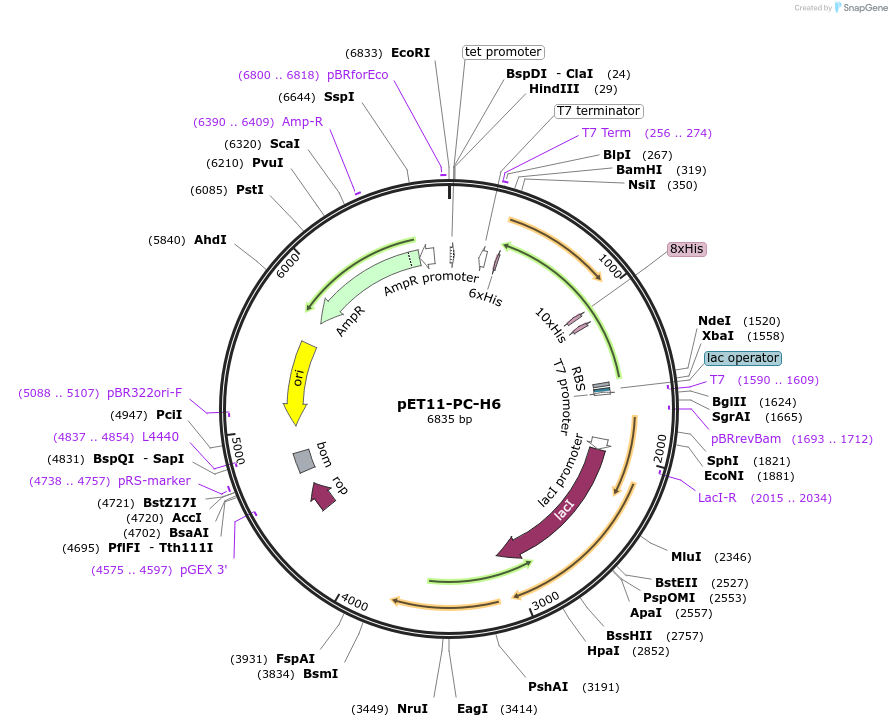
pET11-PC-H6
(Plasmid
#183777)
-
PurposeExpress PC-H6 in E. coli. Purified PC-H6 was used for for generating antibodies in rabbits and for GST-CBP pull-down assays.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 183777 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepET-11d
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5680
- Total vector size (bp) 6874
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namePolycomb
-
Alt namePc
-
SpeciesD. melanogaster (fly)
-
Insert Size (bp)1170
-
Entrez GenePc (a.k.a. Dmel_CG32443, CG32443, CG7618, DmPc, Dmel\CG32443, PC, Pc-G, PcG, dPC, pc)
- Promoter T7
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- 6 His tag at the C-terminus
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NdeI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NsiI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer ATGACTGGTCGAGGCAAGGGG
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byfull length of PC clone (RE66837) was from the Berkeley Drosophila Genome Resource Center.
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pET11-PC-H6 was a gift from Peter Harte (Addgene plasmid # 183777 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:183777 ; RRID:Addgene_183777) -
For your References section:
Polycomb inhibits histone acetylation by CBP by binding directly to its catalytic domain. Tie F, Banerjee R, Fu C, Stratton CA, Fang M, Harte PJ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 9;113(6):E744-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515465113. Epub 2016 Jan 22. 10.1073/pnas.1515465113 PubMed 26802126