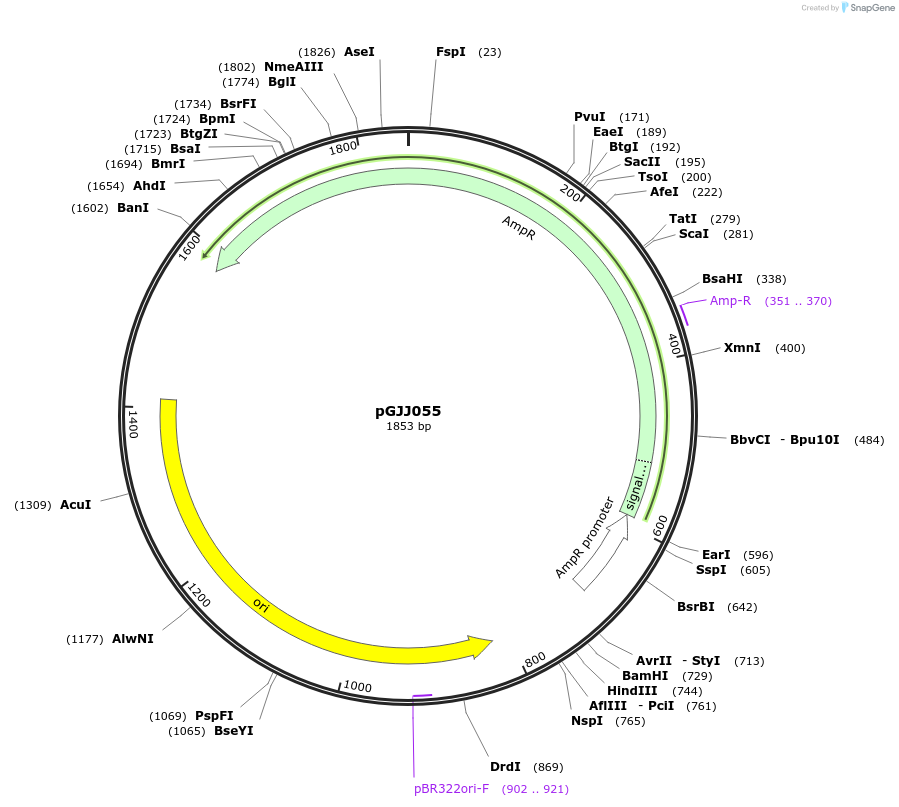
pGJJ055
(Plasmid
#183622)
-
Purpose(Empty Backbone) ddPCA mutagenesis plasmid - Efficient mutant library cloning plasmid suitable for oligo synthesis, error prone PCR or nicking mutagenesis strategies.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 183622 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepUC19
-
Backbone manufacturerNEB
- Backbone size (bp) 2686
-
Modifications to backboneReduced in size by deleting the LacZ-alpha. Modified to harbour a landing site with HindIII and AvrII restriction sites so that the CYC promoter and DHFR3 fused to any protein of interest could be cloned into it. Three synonymous mutations were introduced in the Ampicillin resistance cassette to remove BtsαI restriction sites and a T>C synonymous substitution was added in the Ampicillin resistance cassette gene of pGJJ003 to create an Nb.BbvCI restriction site.
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pGJJ055 was a gift from Ben Lehner (Addgene plasmid # 183622 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:183622 ; RRID:Addgene_183622) -
For your References section:
Mapping the energetic and allosteric landscapes of protein binding domains. Faure AJ, Domingo J, Schmiedel JM, Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Diss G, Lehner B. Nature. 2022 Apr;604(7904):175-183. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04586-4. Epub 2022 Apr 6. 10.1038/s41586-022-04586-4 PubMed 35388192